Describe some similarities and differences in the structures of a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid.
Ch.15 Lipids

Timberlake13th EditionChemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134421353Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 15, Problem 9a
For each of the following fatty acids, give the shorthand notation for the number of carbon atoms and double bonds, and classify as saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated:
a. lauric acid
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the molecular structure of lauric acid. Lauric acid is a fatty acid with the chemical formula C12H24O2. It contains 12 carbon atoms and no double bonds.
Determine the shorthand notation for the fatty acid. The shorthand notation is written as the number of carbon atoms followed by a colon and the number of double bonds. For lauric acid, this would be 12:0 (12 carbons and 0 double bonds).
Classify the fatty acid based on the number of double bonds. Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds, monounsaturated fatty acids have one double bond, and polyunsaturated fatty acids have two or more double bonds.
Since lauric acid has no double bonds, classify it as a saturated fatty acid.
Summarize the findings: Lauric acid has a shorthand notation of 12:0 and is classified as a saturated fatty acid.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fatty Acid Structure
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains. They can be classified based on the number of carbon atoms and the presence of double bonds. The shorthand notation typically includes the total number of carbon atoms followed by the number of double bonds, such as 'C12:0' for lauric acid, indicating 12 carbons and no double bonds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Fatty Acids Example 1
Saturation
Saturation refers to the presence of hydrogen atoms in a fatty acid chain. Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between carbon atoms, allowing for the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. In contrast, unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds, which reduce the number of hydrogen atoms. Lauric acid is classified as saturated because it has no double bonds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Example 2
Classification of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are classified into three main categories: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated. Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds, monounsaturated fatty acids have one double bond, and polyunsaturated fatty acids have two or more double bonds. This classification is important for understanding their chemical properties and health implications.
Recommended video:
Guided course
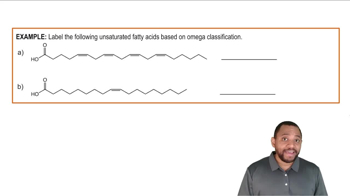
Fatty Acids Example 3
Related Practice
Textbook Question
566
views
Textbook Question
Stearic acid and linoleic acid each have 18 carbon atoms. Why does stearic acid melt at 69 °C but linoleic acid melts at –5 °C?
701
views
Textbook Question
Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following fatty acids:
a. palmitic acid
1321
views
Textbook Question
For each of the following fatty acids, give the shorthand notation for the number of carbon atoms and double bonds, and classify as saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated:
a. linoleic acid
1207
views
Textbook Question
How does the structure of a fatty acid with a cis double bond differ from the structure of a fatty acid with a trans double bond?
675
views
Textbook Question
How does the double bond influence the dispersion forces that can form between the hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids?
718
views
