Draw the condensed structural formula for the ester in jojoba wax that is formed from arachidic acid, a 20-carbon saturated fatty acid, and 1-docosanol, CH3–(CH2)21–OH.
Ch.15 Lipids

Timberlake13th EditionChemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134421353Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 15, Problem 25
Safflower oil is polyunsaturated, whereas olive oil is monounsaturated. Why would safflower oil have a lower melting point than olive oil?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the difference between polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats: Polyunsaturated fats contain multiple double bonds in their fatty acid chains, while monounsaturated fats contain only one double bond.
Recognize that the presence of double bonds introduces kinks in the fatty acid chains, preventing the molecules from packing closely together. Polyunsaturated fats, with more double bonds, have more kinks compared to monounsaturated fats.
Recall that the ability of molecules to pack closely together affects the strength of intermolecular forces, such as London dispersion forces. Molecules that cannot pack closely together have weaker intermolecular forces.
Weaker intermolecular forces result in a lower melting point because less energy is required to overcome these forces and transition the substance from a solid to a liquid state.
Conclude that safflower oil, being polyunsaturated, has more double bonds and kinks in its structure, leading to weaker intermolecular forces and a lower melting point compared to olive oil, which is monounsaturated.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fatty Acid Structure
The structure of fatty acids significantly influences the physical properties of oils. Safflower oil contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, which have multiple double bonds in their carbon chains, leading to kinks that prevent tight packing. In contrast, olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, which have one double bond, allowing for a more linear structure that can pack more closely together.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Fatty Acids Example 1
Melting Point and Saturation
The melting point of fats and oils is affected by their saturation levels. Oils with higher levels of unsaturation, like safflower oil, generally have lower melting points because the kinks in their fatty acid chains disrupt the ability to form solid structures. Conversely, the more saturated structure of olive oil allows for stronger intermolecular forces, resulting in a higher melting point.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Boiling Point Elevation Concept 1
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces, play a crucial role in determining the melting point of oils. In safflower oil, the presence of multiple double bonds reduces the strength of these forces due to the less efficient packing of molecules. Olive oil, with its more saturated composition, experiences stronger intermolecular attractions, contributing to its higher melting point.
Recommended video:
Guided course
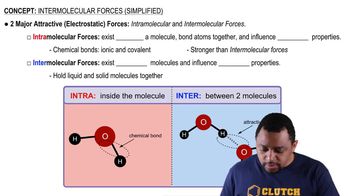
Intermolecular Forces (Simplified) Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
803
views
Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural formula for a triacylglycerol that contains stearic acid and glycerol.
774
views
Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural formula for a mixed triacylglycerol that contains two palmitic acid molecules and one oleic acid molecule on the center carbon of glycerol.
886
views
Textbook Question
How does the percentage of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids in olive oil compare to that of canola oil?
674
views
Textbook Question
Identify each of the following processes as hydrogenation, hydrolysis, or saponification and give the products:
a. the reaction of palm oil with KOH
808
views
Textbook Question
Identify each of the following processes as hydrogenation, hydrolysis, or saponification and give the products:
b. the reaction of glyceryl trilinoleate from safflower oil with water and HCl
1424
views
