Textbook Question
Maltase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes maltose to two glucose molecules.
b. Draw an energy diagram for the reaction with and without maltase.
722
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
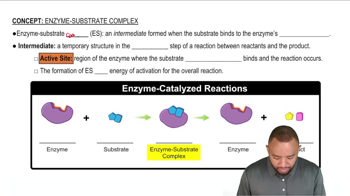


Maltase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes maltose to two glucose molecules.
b. Draw an energy diagram for the reaction with and without maltase.
Indicate whether each of the following would be a substrate (S) or an enzyme (E):
a. glucose
Give the substrate of each of the following enzymes:
a. urease
How would the lock-and-key model explain that sucrase hydrolyzes sucrose, but not lactose?
If a blood test indicates a high level of ALT, what could be the cause?
Consider the amino acids lysine, valine, and aspartate in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
b. be found in hydrophilic regions