Textbook Question
Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
c. How many grams of sulfur would be a typical amount in a 60.-kg adult?
685
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
c. How many grams of sulfur would be a typical amount in a 60.-kg adult?
Using the Chemistry Link to Health: Elements Essential to Health, answer each of the following:
a. What is a micromineral?
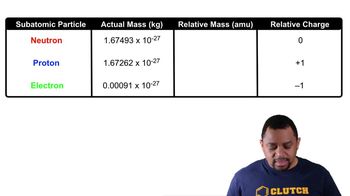
Identify each of the following as describing either a proton, a neutron, or an electron:
a. has the smallest mass
On a dry day, your hair flies apart when you brush it. How would you explain this?
Sometimes clothes cling together when removed from a dryer. What kinds of charges are on the clothes?
Would you use the atomic number, mass number, or both to determine each of the following?
c. number of particles in the nucleus