Textbook Question
What noble gas has the same electron arrangement as the magnesium ion?
1074
views


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

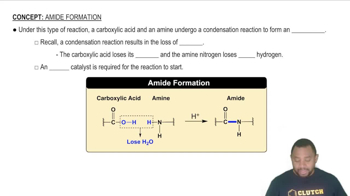
What noble gas has the same electron arrangement as the magnesium ion?
Why are Group 1A (1) and Group 2A (2) elements found in many compounds, but not Group 8A (18) elements?
Consider the following Lewis symbols for elements X and Y:
b. Will a compound of X and Y be ionic or molecular?
Consider the following Lewis symbols for elements X and Y:
d. What would be the formula of a compound of X and Y?
Consider the following Lewis symbols for elements X and Y:
e. What would be the formula of a compound of X and sulfur?
Consider the following Lewis symbols for elements X and Y:
g. Is the compound in part f ionic or molecular?