In Exercises 31–42, solve by the method of your choice. Identify systems with no solution and systems with infinitely many solutions, using set notation to express their solution sets. x + 3y = 2 3x + 9y = 6
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Two Variable Systems of Linear Equations
Problem 41
Textbook Question
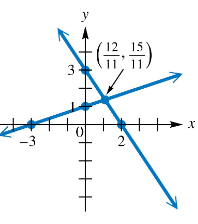
Determine the system of equations illustrated in each graph. Write equations in standard form.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the two lines and their key points from the graph. The first line passes through points (0, 7) and (-4, 0). The second line passes through points (0, 2) and (6, 0).
Find the slope of the first line using the formula \(m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}\). Using points (0, 7) and (-4, 0), calculate \(m_1 = \frac{0 - 7}{-4 - 0} = \frac{-7}{-4} = \frac{7}{4}\).
Use the point-slope form of a line equation \(y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)\) with point (0, 7) and slope \(\frac{7}{4}\) to write the equation of the first line: \(y - 7 = \frac{7}{4}(x - 0)\).
Convert the first line's equation to standard form \(Ax + By = C\) by multiplying both sides to clear fractions and rearranging terms.
Repeat the process for the second line: find slope \(m_2 = \frac{0 - 2}{6 - 0} = \frac{-2}{6} = -\frac{1}{3}\), use point-slope form with point (0, 2), then convert to standard form.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Finding the Equation of a Line from Two Points
To find the equation of a line, use two points on the line to calculate the slope (m) as the change in y over the change in x. Then apply the point-slope form y - y1 = m(x - x1) to write the equation. This method is essential for determining the line's equation from graph points.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Finding Equations of Lines Given Two Points
Converting to Standard Form of a Linear Equation
Standard form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers, and A ≥ 0. After finding the slope-intercept form, rearrange terms to get all variables on one side and the constant on the other. This form is often required for system of equations problems.
Recommended video:
Converting Standard Form to Vertex Form
Interpreting Graphs to Identify Key Points
Graphs provide visual data such as intercepts and points where lines cross. Identifying these points accurately is crucial for writing equations. For example, x- and y-intercepts give direct points to use in slope calculations and equation formulation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Equations of Two Variables by Plotting Points

 4:27m
4:27mWatch next
Master Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
