Express each sum using summation notation. Use a lower limit of summation of your choice and k for the index of summation. a+ar+ar2+⋯+ ar12
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
9. Sequences, Series, & Induction
Sequences
Problem 64
Textbook Question
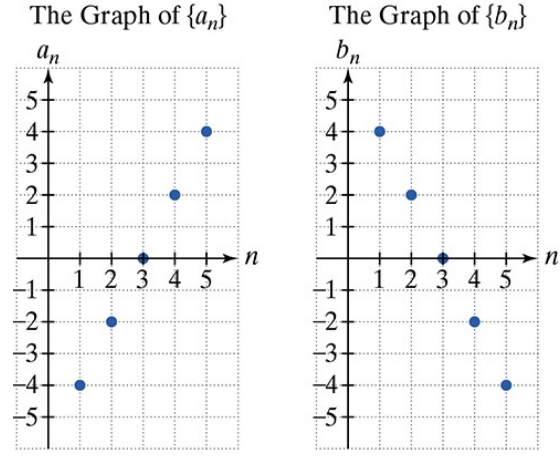
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the values of the sequences \(a_n\) and \(b_n\) for \(n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5\) from the graphs. For \(a_n\), read the y-values of the points at \(n=1, 2, 3, 4, 5\). For \(b_n\), do the same for the corresponding \(n\) values.
Step 2: Write down the values explicitly. For example, \(a_1 = \text{value from graph}\), \(a_2 = \text{value from graph}\), and so on, similarly for \(b_1, b_2, b_3, b_4, b_5\).
Step 3: Calculate each term inside the summation \(a_i + 3b_i\) for \(i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5\). This means multiply each \(b_i\) by 3 and then add the corresponding \(a_i\).
Step 4: Sum all the calculated terms from Step 3 to find \(\sum_{i=1}^5 (a_i + 3b_i)\). This involves adding the five values obtained for each \(i\).
Step 5: Write the final expression for the sum, showing the addition of all terms explicitly, but do not compute the numerical total as per instructions.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sequences and Terms
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers, where each number is called a term. The term a_n represents the nth term of sequence a, and similarly b_n for sequence b. Understanding how to identify and interpret terms from graphs is essential for working with sequences.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Sequences
Summation Notation (Sigma Notation)
Summation notation, represented by the Greek letter sigma (Σ), is a concise way to express the sum of a sequence of terms. For example, Σ from i=1 to 5 of (a_i + 3b_i) means adding the values of a_i plus three times b_i for i = 1 through 5.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Using Graphs to Extract Sequence Values
Graphs of sequences plot term indices on the x-axis and term values on the y-axis. To find specific terms like a_i or b_i, locate the point at x = i and read the corresponding y-value. This skill is crucial for evaluating sums involving terms from graphical data.
Recommended video:
Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations

 8:22m
8:22mWatch next
Master Introduction to Sequences with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
699
views
