Solve each problem. See Example 2. Callie took 20 min to drive her boat upstream to water-ski at her favorite spot. Coming back later in the day, at the same boat speed, took her 15 min. If the current in that part of the river is 5 km per hr, what was her boat speed?
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Equations
Problem 35
Textbook Question
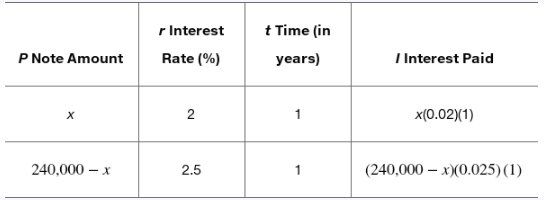
Solve each problem. See Example 4. Cody sells some property for \$240,000. The money will be paid off in two ways: a short-term note at 2% interest and a long-term note at 2.5%. Find the amount of each note if the total annual interest paid is \$5500.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Define variables for the amounts of the two notes. Let \(x\) be the amount of the short-term note at 2% interest, and \(y\) be the amount of the long-term note at 2.5% interest.
Write an equation representing the total amount of the property sold: \(x + y = 240000\).
Write an equation representing the total annual interest paid. The interest from the short-term note is \$0.02x\( and from the long-term note is \)0.025y\(. The total interest is \)5500\(, so the equation is \)0.02x + 0.025y = 5500$.
Use the first equation to express one variable in terms of the other, for example, \(y = 240000 - x\).
Substitute this expression for \(y\) into the interest equation and solve for \(x\). Once \(x\) is found, substitute back to find \(y\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
9mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Simple Interest Formula
Simple interest is calculated using the formula I = P × r × t, where I is the interest, P is the principal amount, r is the interest rate, and t is the time in years. Understanding this formula is essential to relate the interest earned from each note to its principal and rate.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
System of Linear Equations
A system of linear equations involves two or more equations with multiple variables. Solving such systems helps find unknown values—in this case, the amounts of the short-term and long-term notes—by using methods like substitution or elimination.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations
Total Amount Constraint
The total amount of the property sold ($240,000) is split between two notes. This constraint forms one equation where the sum of the two note amounts equals the total sale price, providing a key relationship to solve the problem.
Recommended video:

Probability of Non-Mutually Exclusive Events Example

 7:48m
7:48mWatch next
Master Introduction to Solving Linear Equtions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
449
views
