Find the horizontal asymptote of each function.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Asymptotes
Problem 11
Textbook Question
Use the graph of the rational function in the figure shown to complete each statement in Exercises 9–14.
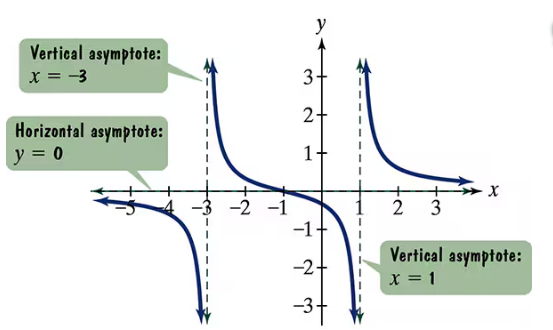
As ______
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the point of interest on the x-axis, which is \(x \to 1^-\), meaning we are approaching 1 from the left side.
Look at the graph near \(x = 1\) and observe the behavior of the function \(f(x)\) as \(x\) approaches 1 from values less than 1.
Notice that the graph is very close to the horizontal asymptote \(y = 0\) near \(x = 1\), and the function values are slightly below zero.
Since the function values are approaching zero from the negative side as \(x\) approaches 1 from the left, we conclude that \(f(x) \to 0^-\) as \(x \to 1^-\).
Therefore, the limit of \(f(x)\) as \(x\) approaches 1 from the left is 0, but the function values are slightly negative.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vertical Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes occur where a function approaches infinity or negative infinity as the input approaches a specific value. They indicate values of x where the function is undefined, often due to division by zero in rational functions. In the graph, vertical asymptotes are shown at x = 6 and x = 14.
Recommended video:

Determining Vertical Asymptotes
Horizontal Asymptotes
A horizontal asymptote represents the value that a function approaches as x approaches positive or negative infinity. It shows the end behavior of the function. In this graph, the horizontal asymptote is y = 0, meaning the function values get closer to zero as x becomes very large or very small.
Recommended video:

Determining Horizontal Asymptotes
Limit Behavior Near a Point
The limit of a function as x approaches a specific value from the left or right describes the function's behavior near that point. For example, as x approaches 1 from the left (x → 1⁻), the function value approaches a certain number or infinity. Understanding this helps in analyzing function continuity and asymptotic behavior.
Recommended video:

Identifying Intervals of Unknown Behavior

 6:24m
6:24mWatch next
Master Introduction to Asymptotes with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
552
views
1
rank
