Find the zeros for each polynomial function and give the multiplicity for each zero. State whether the graph crosses the x-axis, or touches the x-axis and turns around, at each zero. f(x)=2(x−5)(x+4)2
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 27
Textbook Question
Use an end behavior diagram, as shown below, to describe the end behavior of the graph of each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=3+2x-4x2-5x10




 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the degree and leading coefficient of the polynomial function. The given function is \(f(x) = 3 + 2x - 4x^2 - 5x^{10}\). The term with the highest power of \(x\) is \(-5x^{10}\), so the degree is 10 and the leading coefficient is \(-5\).
Determine the end behavior based on the degree and leading coefficient. Since the degree is even (10) and the leading coefficient is negative (\(-5\)), the ends of the graph will both point downwards.
Express the end behavior in terms of limits: As \(x \to \infty\), \(f(x) \to -\infty\) and as \(x \to -\infty\), \(f(x) \to -\infty\).
Draw or visualize the end behavior diagram: both ends of the graph go down towards negative infinity.
Summarize the end behavior: The graph falls to negative infinity on both the left and right ends because the leading term dominates the behavior for very large positive and negative values of \(x\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Functions and Degree
A polynomial function is an expression consisting of variables raised to whole-number exponents and their coefficients. The degree of the polynomial is the highest exponent of the variable, which largely determines the shape and end behavior of its graph.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Leading Term and Leading Coefficient
The leading term of a polynomial is the term with the highest degree, and its coefficient is the leading coefficient. These determine the end behavior of the polynomial's graph, indicating how the function behaves as x approaches positive or negative infinity.
Recommended video:
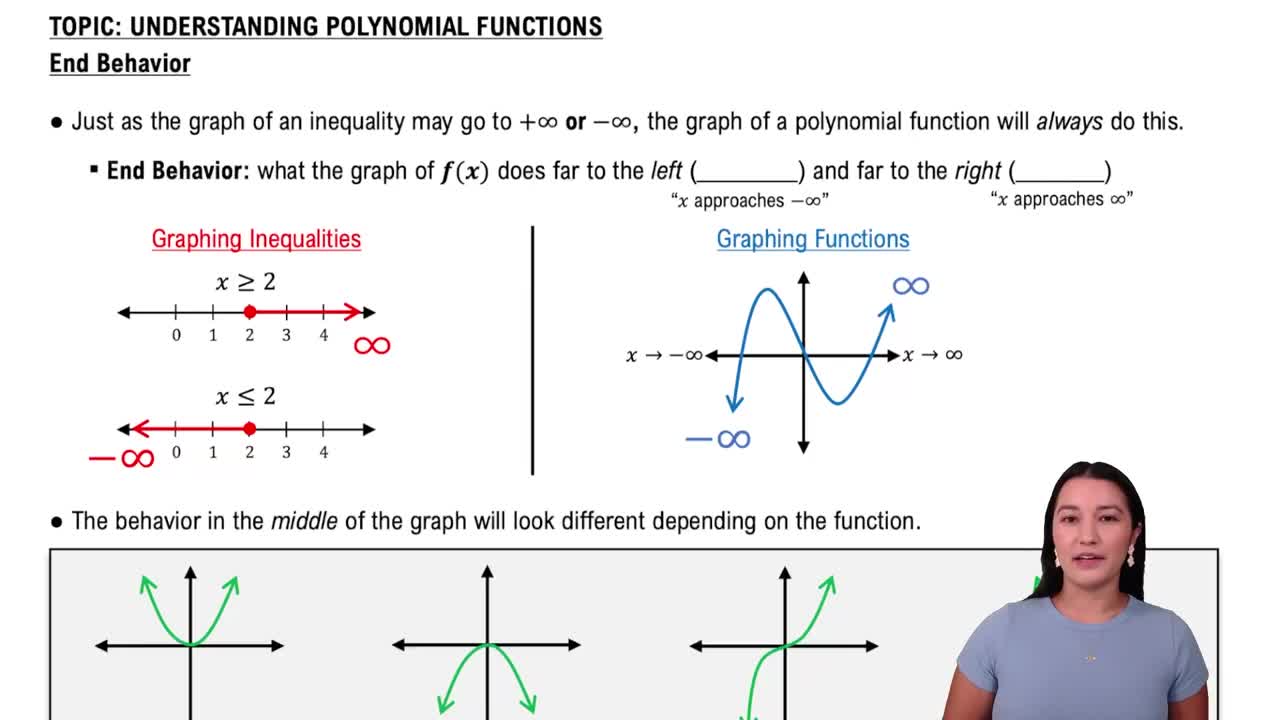
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions
End Behavior of Polynomial Graphs
End behavior describes how the values of a polynomial function behave as x approaches infinity or negative infinity. It depends on the degree and leading coefficient: even-degree polynomials with positive leading coefficients rise on both ends, while odd-degree polynomials have opposite end behaviors.
Recommended video:

End Behavior of Polynomial Functions

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1054
views
