Find the distance between each pair of points, and give the coordinates of the midpoint of the line segment joining them. A(-6, 3), B(-6,8)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Intro to Functions & Their Graphs
Problem 79
Textbook Question
Find the domain of each function.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the function given: \(f(x) = \frac{x}{x^2 + 4x - 21}\).
Recall that the domain of a function includes all real numbers except where the denominator is zero, because division by zero is undefined.
Set the denominator equal to zero to find the values to exclude: \(x^2 + 4x - 21 = 0\).
Factor the quadratic equation: find two numbers that multiply to \(-21\) and add to \$4\(. This gives \)(x + 7)(x - 3) = 0$.
Solve each factor for zero: \(x + 7 = 0\) gives \(x = -7\), and \(x - 3 = 0\) gives \(x = 3\). These values are excluded from the domain.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For rational functions, the domain excludes values that make the denominator zero, as division by zero is undefined.
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
Factoring involves rewriting a quadratic expression as a product of two binomials. This helps identify the roots or zeros of the quadratic, which are critical for determining values that make the denominator zero in rational functions.
Recommended video:
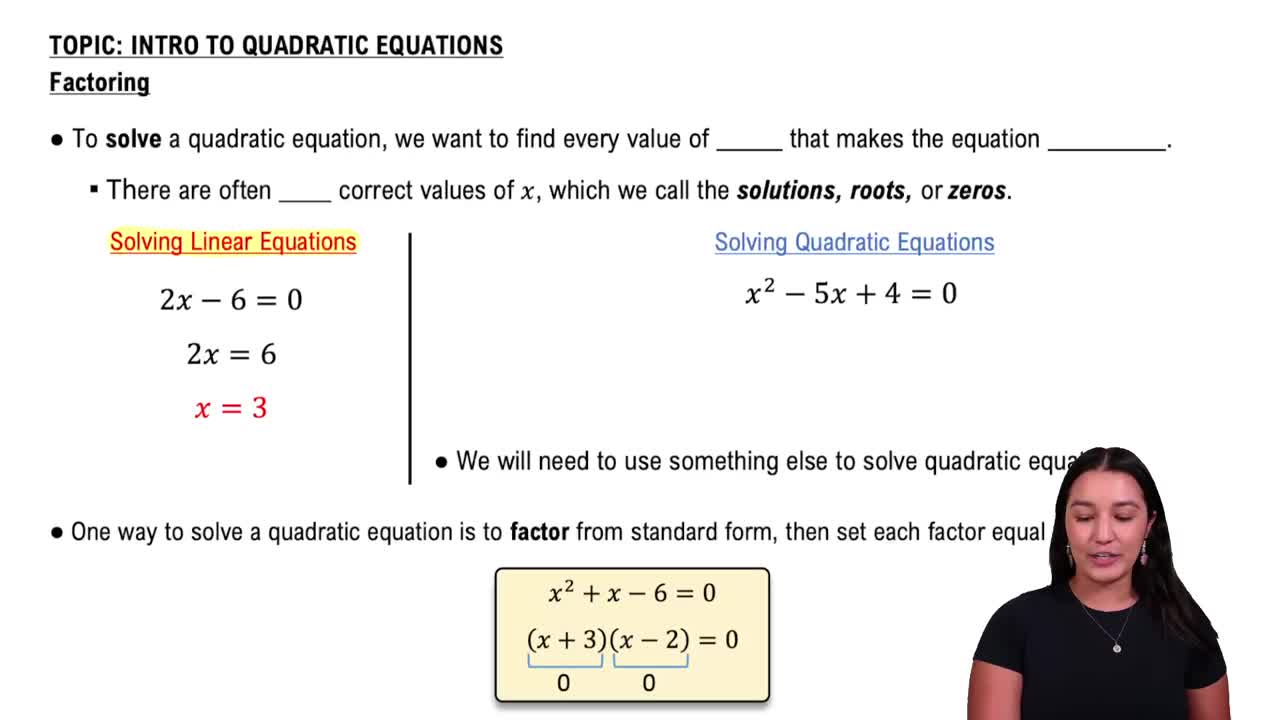
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Solving Quadratic Equations
Solving quadratic equations means finding the values of x that satisfy the equation when set equal to zero. These solutions indicate points where the denominator of a rational function is zero and must be excluded from the domain.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring

 5:2m
5:2mWatch next
Master Relations and Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
417
views
