Solve each equation using the quadratic formula. x2 - 6x = -7
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Square Root Property
Problem 3
Textbook Question
Match the equation in Column I with its solution(s) in Column II. x2 + 5 = 0
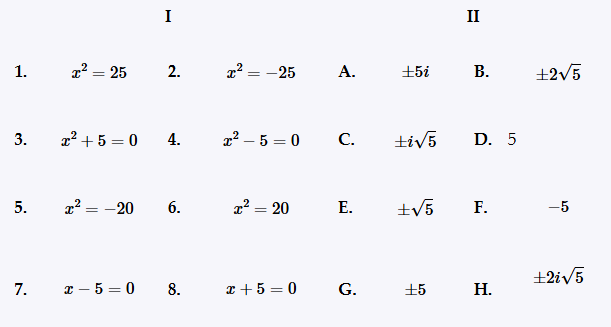
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start with the given equation: \(x^2 + 5 = 0\).
Isolate the \(x^2\) term by subtracting 5 from both sides: \(x^2 = -5\).
Recognize that \(x^2 = -5\) has no real solutions because the square of a real number cannot be negative.
To find the solutions, take the square root of both sides, remembering to include both the positive and negative roots: \(x = \pm \sqrt{-5}\).
Express the square root of a negative number using imaginary numbers: \(x = \pm \sqrt{5}i\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit with the property \(i^2 = -1\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solving Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree two, typically in the form ax² + bx + c = 0. Solving it involves finding values of x that satisfy the equation, often by factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula.
Recommended video:
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Imaginary and Complex Numbers
When a quadratic equation has no real solutions (e.g., when the discriminant is negative), solutions involve imaginary numbers. The imaginary unit i is defined as √-1, allowing solutions to be expressed as complex numbers with real and imaginary parts.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Complex Numbers
Discriminant and Nature of Roots
The discriminant (Δ = b² - 4ac) determines the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation. If Δ < 0, the equation has two complex conjugate solutions; if Δ = 0, one real repeated root; if Δ > 0, two distinct real roots.
Recommended video:

The Discriminant

 6:12m
6:12mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
702
views
