Show that the real zeros of each polynomial function satisfy the given conditions. ƒ(x)=3x4+2x3-4x2+x-1; no real zero greater than 1
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 65
Textbook Question
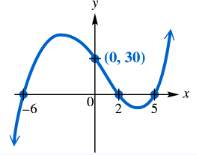
Find a polynomial function f of least degree having the graph shown. (Hint: See the NOTE following Example 4.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the x-intercepts (roots) of the polynomial from the graph. The graph crosses the x-axis at approximately x = -5, x = 1, and x = 4. These are the zeros of the polynomial.
Step 2: Determine the multiplicity of each root by observing the behavior of the graph at each x-intercept. Since the graph crosses the x-axis at each root (not just touches), each root has an odd multiplicity, most likely 1 for the least degree polynomial.
Step 3: Write the general form of the polynomial using the roots. Since the roots are -5, 1, and 4, the polynomial can be expressed as \(f(x) = a(x + 5)(x - 1)(x - 4)\), where \(a\) is a constant coefficient to be determined.
Step 4: Use the given point on the graph, which is the y-intercept at (0, 20), to find the value of \(a\). Substitute \(x = 0\) and \(f(0) = 20\) into the polynomial: \$20 = a(0 + 5)(0 - 1)(0 - 4)$.
Step 5: Solve the equation from Step 4 for \(a\) to find the leading coefficient. Then write the final polynomial function \(f(x)\) by substituting \(a\) back into the general form.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Function and Degree
A polynomial function is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication, with non-negative integer exponents. The degree of the polynomial is the highest exponent of the variable, which determines the general shape and number of turning points of the graph.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Zeros and Multiplicity
Zeros of a polynomial are the x-values where the function equals zero, corresponding to x-intercepts on the graph. The multiplicity of a zero affects the graph's behavior at that point: odd multiplicities cross the x-axis, while even multiplicities touch and turn around without crossing.
Recommended video:

Finding Zeros & Their Multiplicity
Using Points to Determine Coefficients
Known points on the graph, such as the y-intercept, help determine the coefficients of the polynomial. Substituting these points into the polynomial equation allows solving for unknown constants, ensuring the polynomial fits the given graph accurately.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Determinants of 2×2 Matrices

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
456
views
