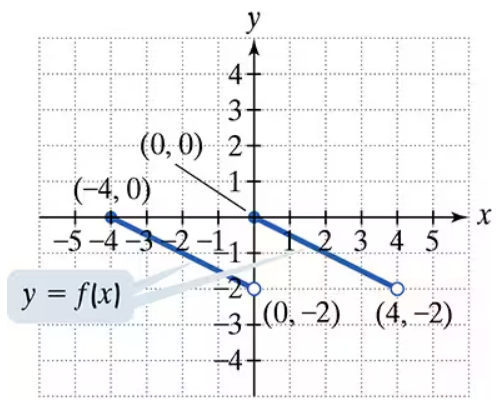
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = −ƒ( x/2) +1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 5:57m
5:57mMaster Graphs of Common Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning