In Exercises 60–63, begin by graphing the standard quadratic function, f(x) = x2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. r(x) = -(x + 1)2
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Common Functions
Problem 39
Textbook Question
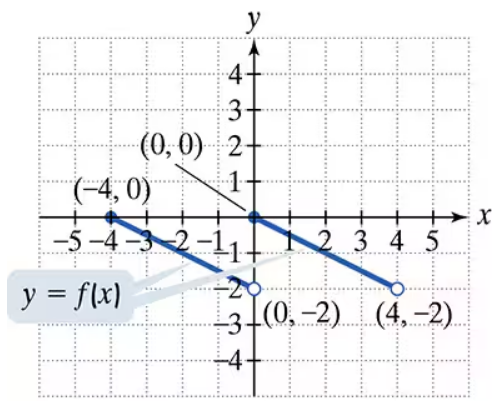
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = -(1/2)f(x+2)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the transformations applied to the function f(x). The given function g(x) = -(1/2)f(x+2) involves three transformations: a horizontal shift, a vertical scaling, and a reflection.
Step 2: Start with the horizontal shift. The term (x+2) inside f(x) indicates a horizontal shift to the left by 2 units. This means every point on the graph of f(x) will move 2 units to the left.
Step 3: Apply the vertical scaling. The coefficient (1/2) in front of f(x+2) compresses the graph vertically by a factor of 1/2. This means the y-coordinates of all points on the graph will be halved.
Step 4: Apply the reflection. The negative sign in front of (1/2) reflects the graph across the x-axis. This means the y-coordinates of all points will be multiplied by -1, flipping the graph upside down.
Step 5: Combine all transformations. Start with the graph of f(x), shift it 2 units to the left, compress it vertically by a factor of 1/2, and then reflect it across the x-axis. The resulting graph is the graph of g(x).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Transformation
Function transformation refers to the process of altering the graph of a function through various operations, such as shifting, stretching, or reflecting. In the given function g(x) = -(1/2)f(x+2), the transformations include a horizontal shift to the left by 2 units, a vertical compression by a factor of 1/2, and a reflection across the x-axis.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Horizontal Shifts
Horizontal shifts occur when a function is modified by adding or subtracting a value inside the function's argument. For g(x) = f(x+2), the '+2' indicates a shift to the left by 2 units. This means that every point on the graph of f(x) will move leftward, affecting the x-coordinates of the graph.
Recommended video:

Shifts of Functions
Vertical Compression and Reflection
Vertical compression and reflection involve scaling the output of a function and flipping it over the x-axis. In g(x) = -(1/2)f(x+2), the factor of -1 indicates a reflection across the x-axis, while the factor of 1/2 compresses the graph vertically, making it half as tall. This alters the y-values of the function, affecting the overall shape of the graph.
Recommended video:

Reflections of Functions

 5:57m
5:57mWatch next
Master Graphs of Common Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
727
views
