Solve each problem. How long will it take a car to travel 400 mi at an average rate of 50 mph?
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Equations
Problem 10
Textbook Question
Solve each problem. Which one or more of the following cannot be a correct equation to solve a geometry problem, if x represents the length of a rectangle? (Hint: Solve each equation and consider the solution.) A. 2x+2(x- 1) = 14 B. -2x+7(5-x) = 52 C. 5(x+2)+5x = 10 D. 2x+2(x-3) = 22
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the variable and the context. Here, \(x\) represents the length of a rectangle, so \(x\) must be a positive number (greater than zero) because lengths cannot be negative or zero.
Step 2: For each equation, isolate \(x\) by simplifying and solving the equation step-by-step. For example, start by expanding parentheses and combining like terms.
Step 3: After simplifying, solve for \(x\) by isolating it on one side of the equation. This may involve adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing both sides of the equation.
Step 4: Once you find the value(s) of \(x\) for each equation, check if the solution is positive. If \(x\) is zero or negative, that equation cannot represent a valid length of a rectangle and thus cannot be a correct equation for the problem.
Step 5: Summarize which equations yield valid positive solutions for \(x\) and which do not, based on the solutions found in the previous step.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Formulating and Solving Linear Equations
Linear equations involve variables raised only to the first power and can be solved using algebraic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and distribution. Understanding how to isolate the variable and solve for its value is essential to determine if the equation yields a valid solution for the problem.
Recommended video:

Solving Linear Equations with Fractions
Interpreting Solutions in Context
After solving an equation, it is important to interpret the solution within the problem's context. For geometry problems involving lengths, solutions must be positive and make sense physically. Negative or non-real values indicate that the equation cannot represent a valid geometric measurement.
Recommended video:

Probability of Non-Mutually Exclusive Events Example
Distributive Property and Simplification
The distributive property allows multiplication over addition or subtraction inside parentheses, e.g., a(b + c) = ab + ac. Proper use of this property is crucial to simplify equations correctly before solving. Misapplication can lead to incorrect equations or solutions that do not fit the problem.
Recommended video:
Guided course
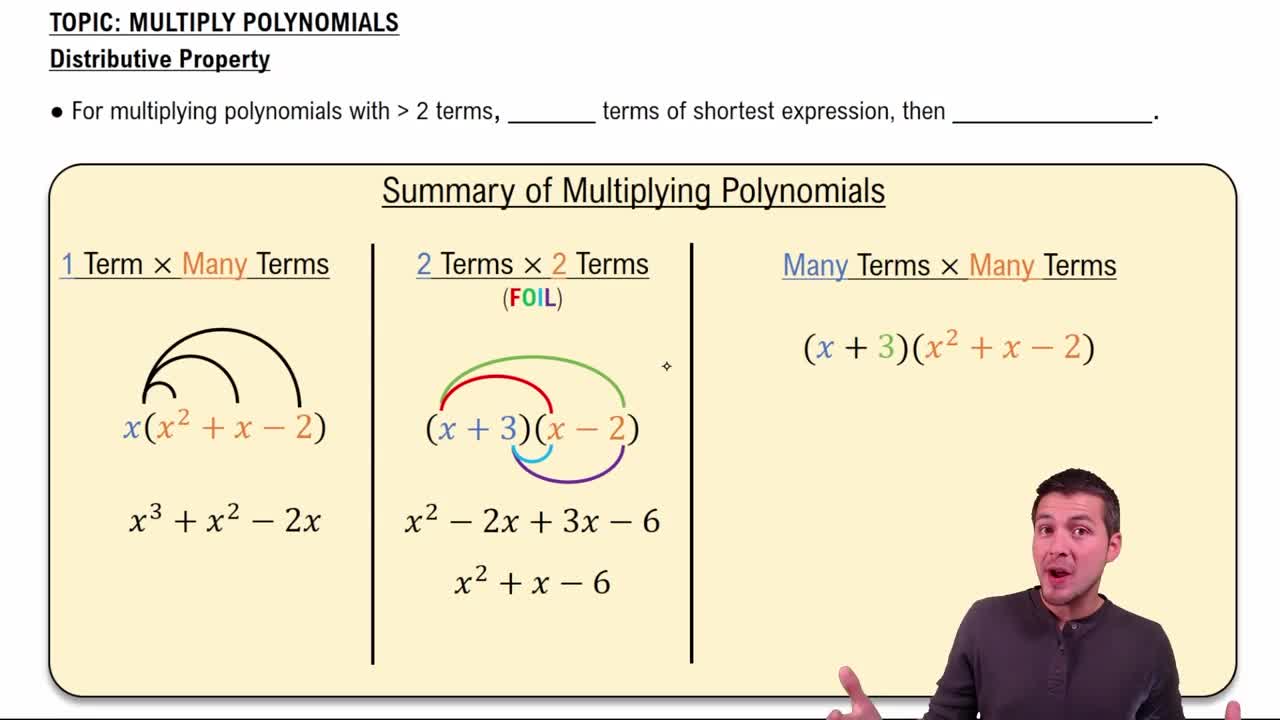
Multiply Polynomials Using the Distributive Property

 7:48m
7:48mWatch next
Master Introduction to Solving Linear Equtions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
453
views
