Graph each function. See Examples 6–8 and the Summary of Graphing Techniques box following Example 9. ƒ(x)=3√x-2
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Transformations
Problem 95
Textbook Question
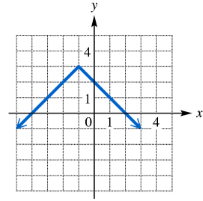
Each of the following graphs is obtained from the graph of ƒ(x)=|x| or g(x)=√x by applying several of the transformations discussed in this section. Describe the transformations and give an equation for the graph.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the base function. The graph resembles the shape of the absolute value function \(f(x) = |x|\), which has a 'V' shape with its vertex at the origin (0,0).
Step 2: Observe the vertex shift. The vertex of the graph is at \((-3, 5)\) instead of at the origin, indicating a horizontal shift 3 units to the left and a vertical shift 5 units up.
Step 3: Analyze the slopes of the lines. The left side of the graph has a positive slope of 1, and the right side has a negative slope of -2, which means the right side is steeper than the left side. This suggests a vertical stretch by a factor of 2 on the right side and no stretch on the left side.
Step 4: Write the piecewise function. Since the graph is based on \(|x|\), which is defined as \(f(x) = -x\) for \(x < 0\) and \(f(x) = x\) for \(x \\geq 0\), apply the transformations:
For \(x < -3\), the function is \(y = (x + 3) + 5\) (shifted left and up). For \(x \\geq -3\), the function is \(y = -2(x + 3) + 5\) (shifted left and up, and vertically stretched by 2 with reflection).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function, f(x) = |x|, produces a V-shaped graph with its vertex at the origin. It outputs the distance of x from zero, always non-negative. Understanding its basic shape helps in identifying transformations like shifts, reflections, and stretches.
Recommended video:

Function Composition
Transformations of Functions
Transformations include shifts (horizontal and vertical), reflections (across axes), stretches, and compressions. These changes alter the graph's position, orientation, or size. Recognizing how each transformation affects the graph is essential for writing the new equation.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Piecewise Linear Functions
A piecewise linear function is defined by different linear expressions over intervals. The graph in the image shows two linear segments joined at a vertex, indicating a transformation of the absolute value function. Understanding piecewise definitions helps in expressing the transformed function accurately.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
649
views
