The thermite reaction, Fe2O3 + Al → Al2O3 + Fe produces so much heat that the Fe product melts. This reaction is used industrially to weld metal parts under water, where a torch cannot be employed. It is also a favorite chemical demonstration in the lecture hall (on a small scale). (b) Calculate how many grams of aluminum are needed to completely react with 500.0 g of Fe2O3 in this reaction.

One of the most bizarre reactions in chemistry is called theUgi reaction:R1C(=O)R2 + R3 - NH2 + R4COOH + R5NC SR4C(=O)N(R3)C(R1R2)C=ONHR5 + H2O
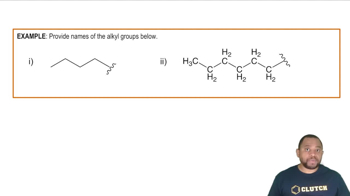
(a) Write out the balanced chemical equation for the Ugi reaction,for the case where R = CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2—(this is called the hexyl group) for all compounds.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Ugi Reaction

Balanced Chemical Equation

Hexyl Group
The thermite reaction, Fe2O3 + Al → Al2O3 + Fe produces so much heat that the Fe product melts. This reaction is used industrially to weld metal parts under water, where a torch cannot be employed. It is also a favorite chemical demonstration in the lecture hall (on a small scale). (c) This reaction produces 852 kJ of heat per mole of Fe2O3 reacted. How many grams of Fe2O3 are needed to produce 1.00 × 104 kJ of heat?
The thermite reaction, Fe2O3 + Al S Al2O3 + Fe produces so much heat that the Fe product melts. This reaction is used industrially to weld metal parts under water, where a torch cannot be employed. It is also a favorite chemical demonstration in the lecture hall (on a small scale). (d) If you performed the reverse reaction— aluminum oxide plus iron makes iron oxide plus aluminum—would that reaction have heat as a reactant or a product?
