Textbook Question
Indicate if the atoms in each pair have the same number of protons, neutrons, or electrons.
c. 4018Ar, 3917Cl
1428
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


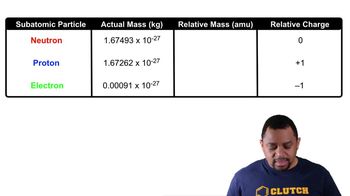
Indicate if the atoms in each pair have the same number of protons, neutrons, or electrons.
c. 4018Ar, 3917Cl
Complete the following table for the three naturally occurring isotopes of silicon, the major component in computer chips:
For each representation of a nucleus A through E, write the atomic symbol and identify which are isotopes.
a. <IMAGE>
Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false:
d. The proton and the electron have about the same mass.
Write the name and symbol of the element with the following atomic number:
h. 92
Why is the ionization energy of Ca higher than K, but lower than that of Mg?