List three indirect methods of counting microbes.

List five direct methods of counting microbes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
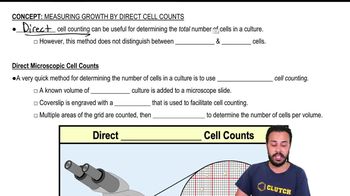
Direct Microscopic Count
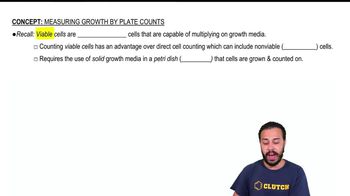
Viable Plate Count
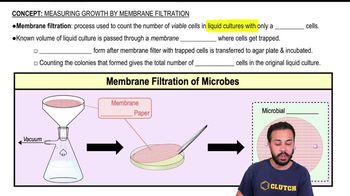
Membrane Filtration
In a defined medium:
a. The exact chemical composition of the medium is known
b. Agar is available for microbial nutrition
c. Blood may be included
d. Organic chemicals are excluded
A student observes a researcher streaking a plate numerous times, flaming the loop between streaks. The researcher is likely using the ___________ method to isolate microorganisms.
Which of the following is most useful in representing population growth on a graph?
a. Logarithmic reproduction of the growth curve
b. A semilogarithmic graph using a log scale on the y-axis
c. An arithmetic graph of the lag phase followed by a logarithmic section for the log, stationary, and death phases
d. None of the above would best represent a population growth curve
Chemolithotrophs acquire electrons from (organic/inorganic)___________ compounds.
Which of the following methods is best for counting fecal bacteria from a stream to determine the safety of the water for drinking?
a. Dry weight
b. Turbidity
c. Viable plate counts
d. Membrane filtration
