Find the standard form of the equation of each parabola satisfying the given conditions. Vertex: (2, - 3); Focus: (2, - 5)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
8. Conic Sections
Parabolas
Problem 33
Textbook Question
Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of each parabola with the given equation. Then match each equation to one of the graphs that are shown and labeled (a)–(d). (x + 1)2 = - 4(y + 1)
a. 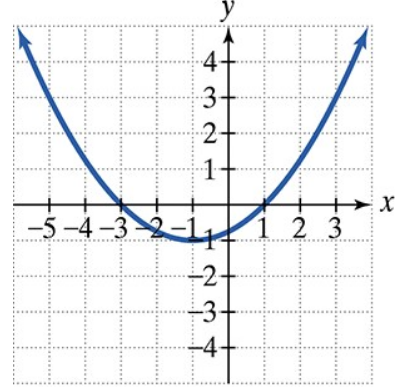 b.
b. 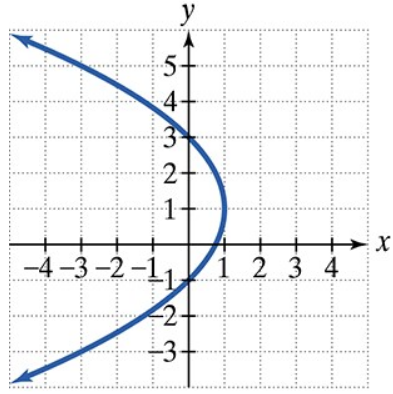 c.
c. 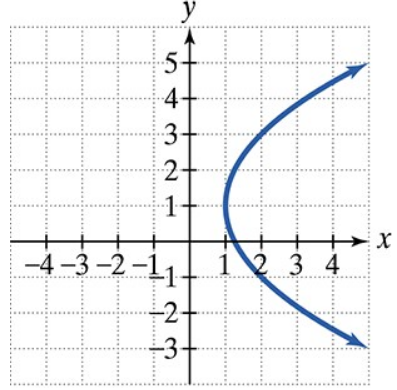 d.
d. 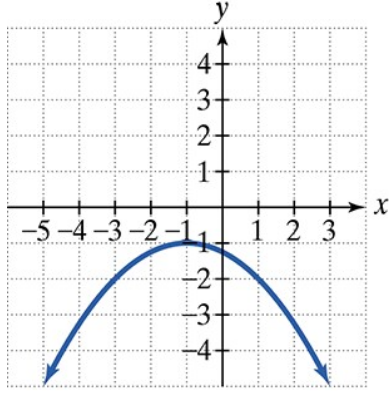
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the form of the given equation. The equation \((x + 1)^2 = -4(y + 1)\) is in the form \((x - h)^2 = 4p(y - k)\), which represents a vertical parabola that opens either up or down.
From the equation, determine the vertex \((h, k)\). Here, \(h = -1\) and \(k = -1\), so the vertex is at \((-1, -1)\).
Find the value of \(p\) by comparing the equation to the standard form. Since \$4p = -4\(, solve for \)p\( to get \)p = -1$. The negative value indicates the parabola opens downward.
Use the vertex and \(p\) to find the focus. The focus lies \(p\) units from the vertex along the axis of symmetry. Since the parabola opens vertically, the focus is at \((h, k + p)\), which is \((-1, -1 - 1)\).
Find the directrix, which is a horizontal line \(p\) units in the opposite direction from the vertex. The directrix is the line \(y = k - p\), or \(y = -1 - (-1)\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Standard Form of a Parabola
The standard form of a parabola's equation helps identify its orientation and key features. For vertical parabolas, the form is (x - h)^2 = 4p(y - k), where (h, k) is the vertex and p indicates the distance from the vertex to the focus and directrix. Recognizing this form allows you to extract important information directly from the equation.
Recommended video:

Parabolas as Conic Sections
Vertex, Focus, and Directrix of a Parabola
The vertex is the parabola's turning point, given by (h, k). The focus lies inside the parabola at a distance p from the vertex along the axis of symmetry. The directrix is a line perpendicular to the axis of symmetry, located p units opposite the focus. These elements define the parabola's shape and position.
Recommended video:

Horizontal Parabolas Example 1
Graph Matching Using Parabola Features
Matching an equation to a graph involves using the vertex, focus, and directrix to determine the parabola's orientation and position. By calculating these features from the equation, you can compare them to the labeled graphs and identify the correct match based on shape, direction (up/down/left/right), and location.
Recommended video:

Parabolas as Conic Sections

 5:33m
5:33mWatch next
Master Parabolas as Conic Sections with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
674
views
