Use the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. 2x3+x+2; x+1
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Zeros of Polynomial Functions
Problem 36
Textbook Question
For each polynomial function, one zero is given. Find all other zeros.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given polynomial function: \(f(x) = 4x^3 + 6x^2 - 2x - 1\), and the known zero: \(x = \frac{1}{2}\).
Use polynomial division or synthetic division to divide \(f(x)\) by the factor corresponding to the known zero, which is \(\left(x - \frac{1}{2}\right)\).
Perform the division to find the quotient polynomial, which will be a quadratic polynomial since the original is cubic.
Set the quotient polynomial equal to zero and solve for the remaining zeros using the quadratic formula: \(x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\), where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are coefficients from the quadratic.
List all zeros: the known zero \(\frac{1}{2}\) and the two zeros found from solving the quadratic equation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
12mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Zeros and Roots
Zeros or roots of a polynomial are the values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero. Finding all zeros involves solving the polynomial equation, which can include real and complex solutions. Knowing one zero helps in factoring the polynomial to find the others.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Polynomial Division (Synthetic or Long Division)
Polynomial division is used to divide a polynomial by a binomial corresponding to a known zero, simplifying the polynomial to a lower degree. Synthetic division is a shortcut method when dividing by linear factors, making it easier to find remaining zeros.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Factoring Polynomials
Factoring and Solving Quadratic Equations
After dividing the polynomial, the quotient is often a quadratic that can be factored or solved using the quadratic formula. This step is essential to find the remaining zeros once the polynomial is reduced to degree two.
Recommended video:
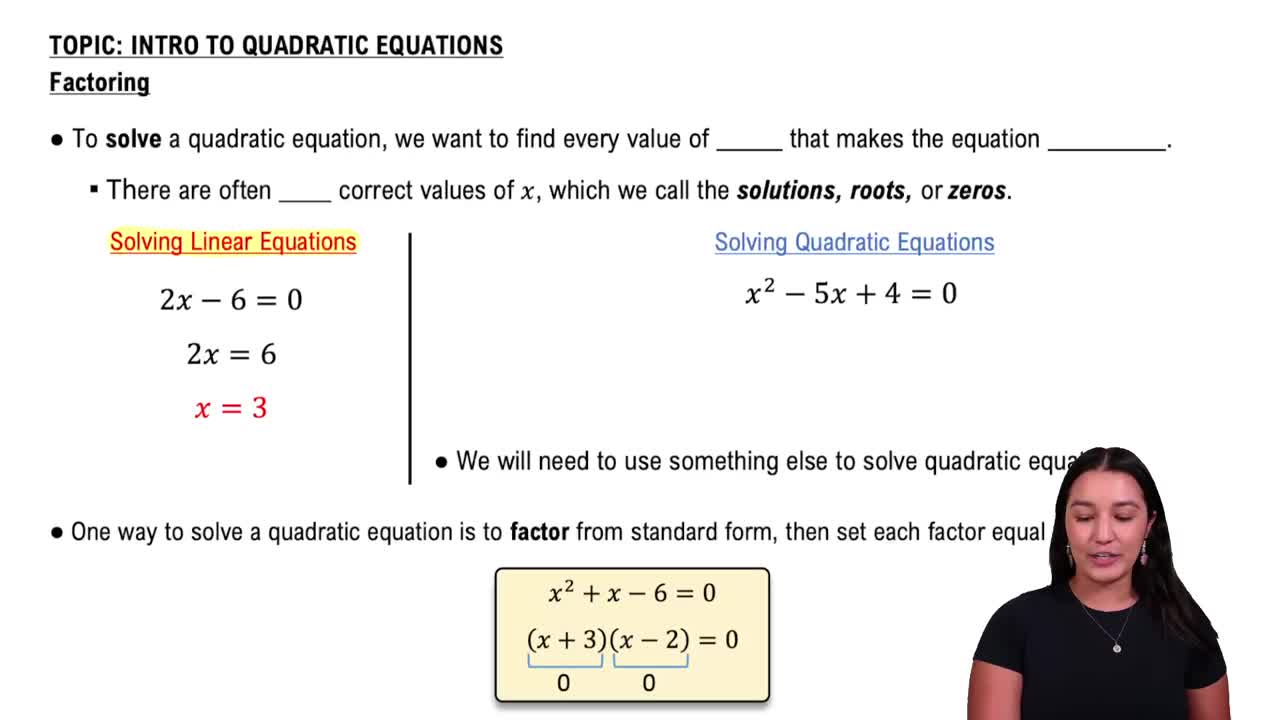
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
498
views
