Factor into linear factors given that k is a zero. (multiplicity )
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Zeros of Polynomial Functions
Problem 48
Textbook Question
For each polynomial function, find all zeros and their multiplicities.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the factors of the polynomial function given: \(f(x) = (x+1)^2 (x-1)^3 (x^2 - 10)\).
Set each factor equal to zero to find the zeros of the function: solve \(x+1=0\), \(x-1=0\), and \(x^2 - 10=0\) separately.
Solve the linear equations: \(x+1=0\) gives \(x=-1\), and \(x-1=0\) gives \(x=1\). These are zeros with multiplicities corresponding to the exponents on their factors.
Solve the quadratic equation \(x^2 - 10 = 0\) by isolating \(x^2\): \(x^2 = 10\), then take the square root of both sides to find \(x = \pm \sqrt{10}\).
Determine the multiplicities of each zero based on the exponents in the original polynomial: \(x=-1\) has multiplicity 2, \(x=1\) has multiplicity 3, and \(x=\pm \sqrt{10}\) each have multiplicity 1.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
7mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Zeros
Zeros of a polynomial are the values of x for which the polynomial equals zero. Finding zeros involves setting the polynomial equal to zero and solving for x. These zeros correspond to the roots or x-intercepts of the polynomial function.
Recommended video:

Finding Zeros & Their Multiplicity
Multiplicity of Zeros
Multiplicity refers to the number of times a particular zero appears as a factor in the polynomial. For example, if (x - a)^k is a factor, then x = a is a zero with multiplicity k. Multiplicity affects the graph's behavior at the zero, such as whether it crosses or touches the x-axis.
Recommended video:

Finding Zeros & Their Multiplicity
Factoring and Solving Quadratic Expressions
Factoring involves expressing a polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials. For quadratic expressions like x^2 - 10, solving for zeros may require techniques such as taking square roots or using the quadratic formula if it cannot be factored easily. This step is essential to find all zeros of the function.
Recommended video:
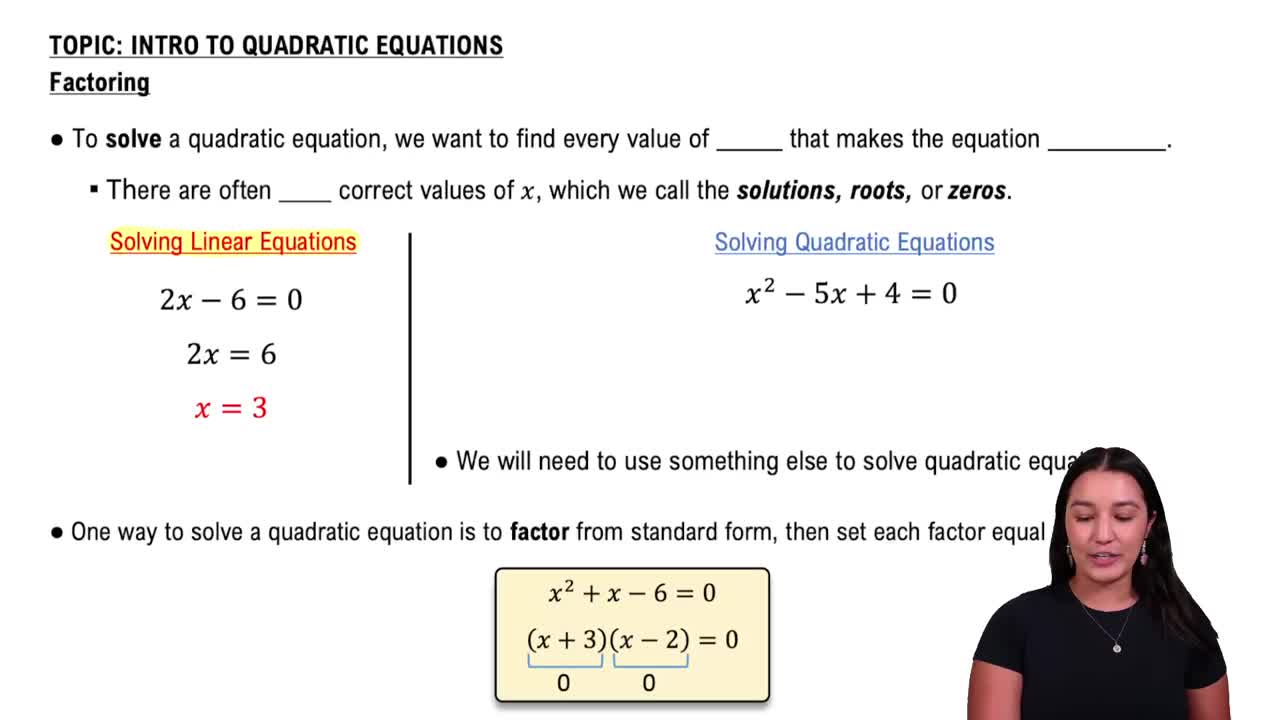
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
338
views
