Solve each radical equation in Exercises 11–30. Check all proposed solutions. √(x + 3) = x - 3
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Choosing a Method to Solve Quadratics
Problem 95
Textbook Question
Use the method described in Exercises 83–86, if applicable, and properties of absolute value to solve each equation or inequality. (Hint: Exercises 99 and 100 can be solved by inspection.) | 4x2 - 23x - 6 | = 0
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recognize that the equation involves an absolute value expression set equal to zero: \(|4x^2 - 23x - 6| = 0\).
Recall the property of absolute value: \(|A| = 0\) if and only if \(A = 0\). This means we can set the inside of the absolute value equal to zero: \$4x^2 - 23x - 6 = 0$.
Solve the quadratic equation \$4x^2 - 23x - 6 = 0\( by using the quadratic formula: \)x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\(, where \)a = 4\(, \)b = -23\(, and \)c = -6$.
Calculate the discriminant \(\Delta = b^2 - 4ac\) to determine the nature of the roots.
Use the values of \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) in the quadratic formula to find the solutions for \(x\), which will be the solutions to the original absolute value equation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Absolute Value and Its Properties
The absolute value of a number represents its distance from zero on the number line, always non-negative. For an expression |A| = 0, the only solution is when A = 0, since absolute value cannot be negative. Understanding this property helps simplify equations involving absolute values.
Recommended video:

Change of Base Property
Solving Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree two, typically in the form ax² + bx + c = 0. Solutions can be found by factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. Identifying and solving the quadratic inside the absolute value is essential here.
Recommended video:
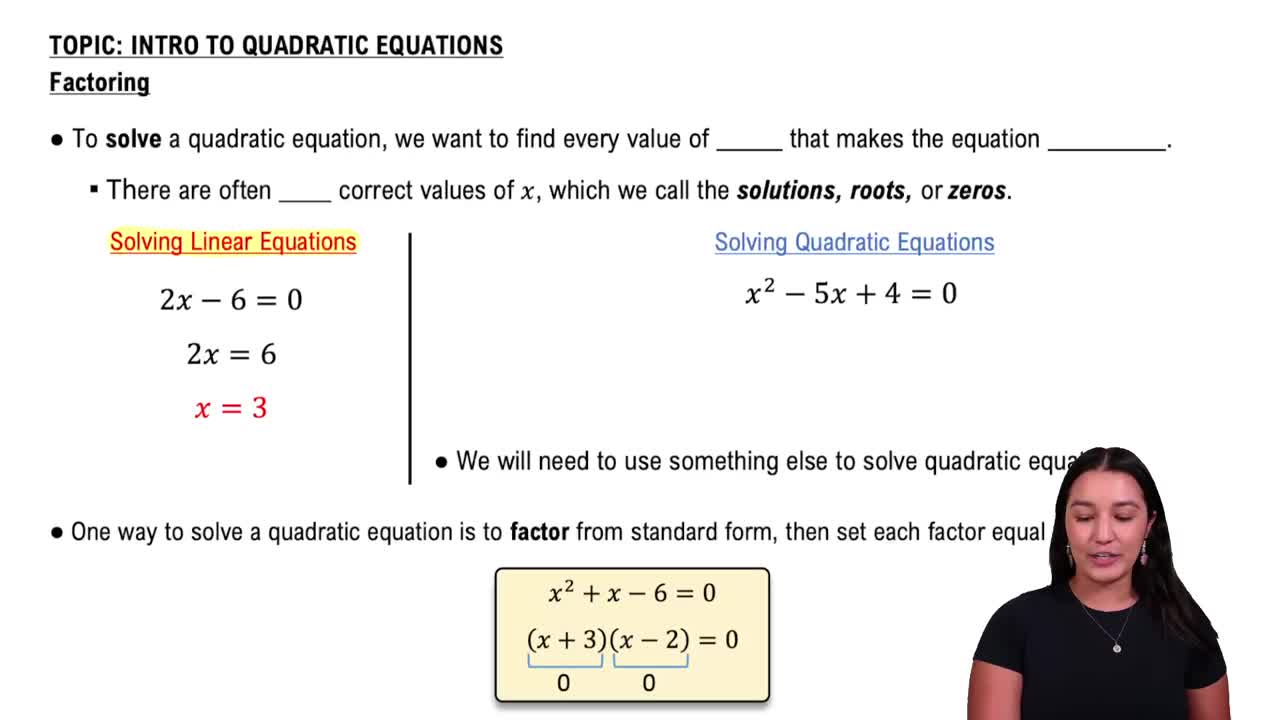
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Equation Solving Strategy for Absolute Value Equations
When solving |f(x)| = 0, set the inside function f(x) equal to zero and solve. For inequalities or other absolute value equations, consider splitting into cases based on the definition of absolute value. This method ensures all possible solutions are found.
Recommended video:

Solving Logarithmic Equations

 4:03m
4:03mWatch next
Master Choosing a Method to Solve Quadratics with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
278
views
