Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to solve Exercises 29–40. An ice cream store sells two drinks (sodas or milk shakes) in four sizes (small, medium, large, or jumbo) and five flavors (vanilla, strawberry, chocolate, coffee, or pistachio). In how many ways can a customer order a drink?
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
10. Combinatorics & Probability
Combinatorics
Problem 25
Textbook Question
Evaluate each expression.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the combinations in the expression: \$7C3\( and \)5C4$. Recall that the combination formula is given by \(nCr = \frac{n!}{r!(n-r)!}\).
Write out each combination using the formula: \(7C3 = \frac{7!}{3!(7-3)!} = \frac{7!}{3!4!}\) and \(5C4 = \frac{5!}{4!(5-4)!} = \frac{5!}{4!1!}\).
Calculate each combination separately by simplifying the factorial expressions. For example, simplify \$7!\(, \)3!\(, and \)4!\( as needed to find \)7C3\(, and similarly for \)5C4$.
Evaluate the factorial fraction \(\frac{98!}{96!}\) by simplifying it. Remember that \(\frac{98!}{96!} = 98 \times 97\) because the factorial terms cancel out except for the last two factors.
Substitute the values of \$7C3\(, \)5C4$, and \(\frac{98!}{96!}\) back into the original expression and perform the subtraction to complete the evaluation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
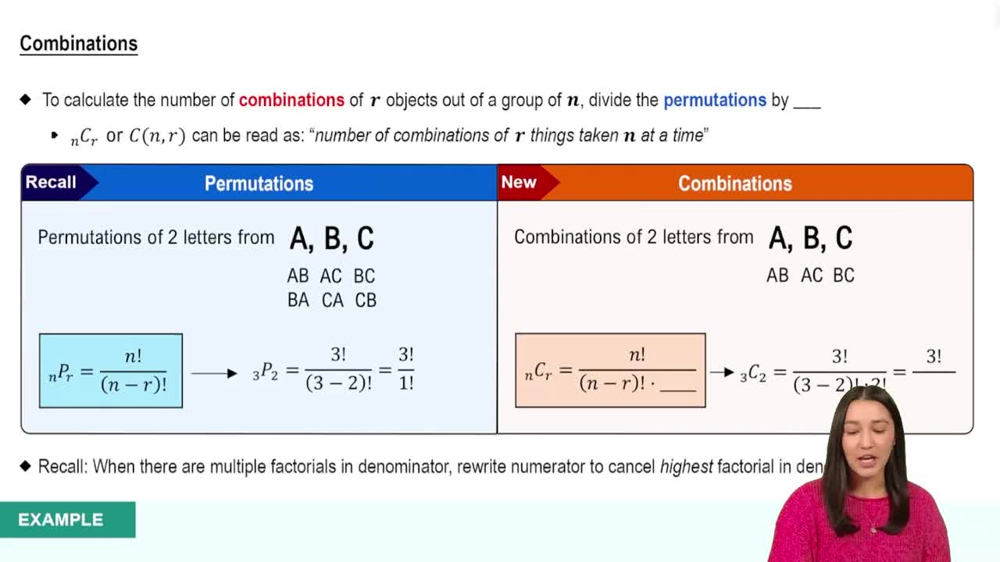
Combination Formula
A combination represents the number of ways to choose a subset of items from a larger set without regard to order. It is calculated using the formula nCr = n! / [r!(n-r)!], where n is the total number of items and r is the number chosen.
Recommended video:
Combinations
Factorials
A factorial, denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers from 1 up to n. Factorials are fundamental in permutations and combinations, simplifying expressions involving counting and arrangements.
Recommended video:

Factorials
Simplifying Factorial Expressions
When evaluating expressions involving factorials, it is often helpful to cancel common terms in the numerator and denominator. This simplification reduces computational complexity and helps in accurately calculating combinations or other factorial-based expressions.
Recommended video:

Factorials
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
565
views


