In Exercises 39-52, a. Find an equation for ƒ¯¹(x). b. Graph ƒ and ƒ¯¹(x) in the same rectangular coordinate system. c. Use interval notation to give the domain and the range off and ƒ¯¹. f(x) = (x+2)³
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Function Composition
Problem 53
Textbook Question
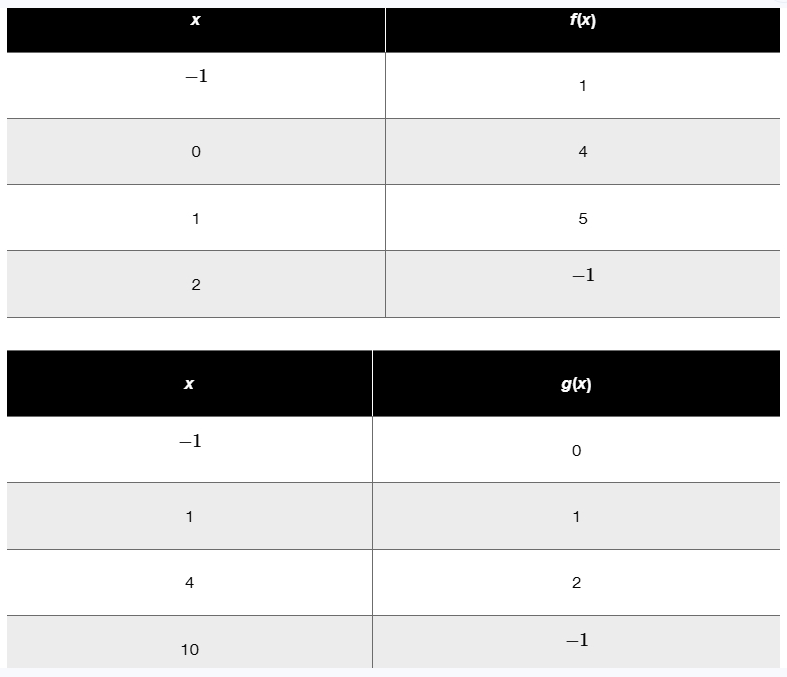
In Exercises 53–58, f and g are defined by the following tables. Use the tables to evaluate each composite function. f(g(1))
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the composite function to evaluate: \(f(g(1))\). This means you first find \(g(1)\), then use that result as the input for \(f\).
Look up the value of \(g(1)\) in the \(g(x)\) table. According to the table, when \(x = 1\), \(g(1) = 1\).
Now, use the value \(g(1) = 1\) as the input for the function \(f\). So, you need to find \(f(1)\).
Look up the value of \(f(1)\) in the \(f(x)\) table. According to the table, when \(x = 1\), \(f(1) = 5\).
Therefore, the value of the composite function \(f(g(1))\) is \(f(1)\), which corresponds to the value found in the previous step.
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Evaluation
Function evaluation involves finding the output value of a function for a given input. Using the tables, you locate the input value in the x-column and read the corresponding function value from the f(x) or g(x) column. This is essential for determining values like g(1) or f(g(1)).
Recommended video:

Evaluating Composed Functions
Composite Functions
A composite function, denoted as f(g(x)), means applying one function to the result of another. First, evaluate the inner function g at x, then use that output as the input for f. Understanding this process is key to correctly evaluating expressions like f(g(1)).
Recommended video:

Function Composition
Using Tables to Represent Functions
Tables provide discrete values of functions for specific inputs, allowing evaluation without explicit formulas. By matching input values to outputs in the tables, you can perform operations like composition. This method is useful when functions are defined only by data points.
Recommended video:
Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations

 4:56m
4:56mWatch next
Master Function Composition with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
449
views
