Graph each function. See Examples 1 and 2. h(x)=|-(1/2)x|
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Transformations
Problem 35
Textbook Question
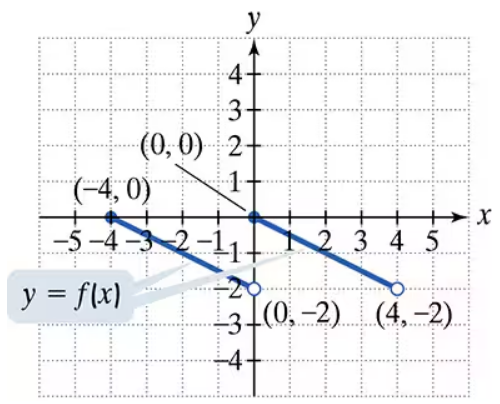
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = f(x+2)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the transformation: The function g(x) = f(x+2) represents a horizontal shift of the graph of f(x). Specifically, adding 2 inside the parentheses shifts the graph 2 units to the left.
Identify key points on the graph of y = f(x): Look at the graph of f(x) and note the coordinates of key points, such as intercepts, peaks, valleys, or other significant points.
Apply the horizontal shift: For each key point (x, y) on the graph of f(x), subtract 2 from the x-coordinate to find the corresponding point on the graph of g(x). The new point will be (x-2, y).
Plot the shifted points: Using the transformed points, plot the new graph of g(x). Ensure that the shape of the graph remains the same as f(x), but shifted 2 units to the left.
Verify the transformation: Double-check that all points and features of the graph of g(x) match the expected transformation of f(x) shifted 2 units to the left.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Transformation
Function transformation refers to the changes made to the graph of a function based on modifications to its equation. In this case, g(x) = f(x + 2) represents a horizontal shift of the function f(x) to the left by 2 units. Understanding how transformations affect the graph is crucial for accurately sketching the new function.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Horizontal Shifts
Horizontal shifts occur when the input variable of a function is altered by adding or subtracting a constant. For g(x) = f(x + 2), the '+2' indicates that every point on the graph of f(x) moves 2 units to the left. This concept is essential for predicting how the graph will change without recalculating every point.
Recommended video:

Shifts of Functions
Graph Interpretation
Graph interpretation involves analyzing the visual representation of a function to understand its behavior and characteristics. By examining the graph of y = f(x), one can identify key features such as intercepts, maxima, and minima, which will help in accurately plotting g(x) after applying the transformation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
566
views
