Graph each function. See Examples 1 and 2. h(x)=|-(1/2)x|
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Transformations
Problem 35
Textbook Question
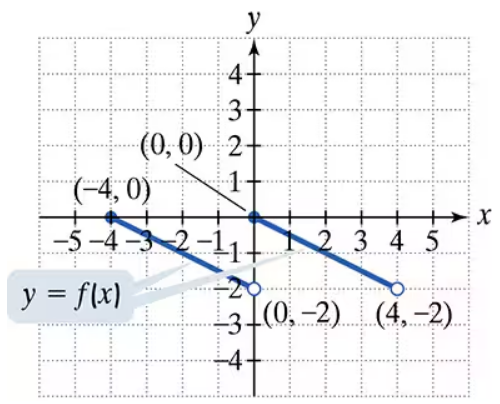
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = f(x+2)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the transformation: The function g(x) = f(x+2) represents a horizontal shift of the graph of f(x). Specifically, adding 2 inside the parentheses shifts the graph 2 units to the left.
Identify key points on the graph of y = f(x): Look at the graph of f(x) and note the coordinates of key points, such as intercepts, peaks, valleys, or other significant points.
Apply the horizontal shift: For each key point (x, y) on the graph of f(x), subtract 2 from the x-coordinate to find the corresponding point on the graph of g(x). The new point will be (x-2, y).
Plot the shifted points: Using the transformed points, plot the new graph of g(x). Ensure that the shape of the graph remains the same as f(x), but shifted 2 units to the left.
Verify the transformation: Double-check that all points and features of the graph of g(x) match the expected transformation of f(x) shifted 2 units to the left.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Transformation
Function transformation refers to the changes made to the graph of a function based on modifications to its equation. In this case, g(x) = f(x + 2) represents a horizontal shift of the function f(x) to the left by 2 units. Understanding how transformations affect the graph is crucial for accurately sketching the new function.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Horizontal Shifts
Horizontal shifts occur when the input variable of a function is altered by adding or subtracting a constant. For g(x) = f(x + 2), the '+2' indicates that every point on the graph of f(x) moves 2 units to the left. This concept is essential for predicting how the graph will change without recalculating every point.
Recommended video:

Shifts of Functions
Graph Interpretation
Graph interpretation involves analyzing the visual representation of a function to understand its behavior and characteristics. By examining the graph of y = f(x), one can identify key features such as intercepts, maxima, and minima, which will help in accurately plotting g(x) after applying the transformation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
567
views
