Use the method described in Exercises 83–86, if applicable, and properties of absolute value to solve each equation or inequality. (Hint: Exercises 99 and 100 can be solved by inspection.) | x2 + 1 | - | 2x | = 0
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Square Root Property
Problem 96
Textbook Question
Answer each question. Find the values of a, b, and c for which the quadratic equation. has the given numbers as solutions. (Hint: Use the zero-factor property in reverse.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recall that if a quadratic equation has solutions (roots) \( r_1 \) and \( r_2 \), then it can be written in factored form as \( a(x - r_1)(x - r_2) = 0 \).
Given the solutions \( -3 \) and \( 2 \), substitute these values into the factored form: \( a(x - (-3))(x - 2) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( a(x + 3)(x - 2) = 0 \).
Expand the factors \( (x + 3)(x - 2) \) by using the distributive property (FOIL method): \( x \cdot x + x \cdot (-2) + 3 \cdot x + 3 \cdot (-2) \).
Simplify the expression from the previous step to get a quadratic expression in standard form: \( x^2 + (\text{sum of coefficients})x + (\text{constant term}) \).
Identify the coefficients \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) from the expanded quadratic expression \( a x^2 + b x + c = 0 \). Note that \( a \) can be any nonzero constant, often taken as 1 for simplicity.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Equation Standard Form
A quadratic equation is expressed as ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants and a ≠ 0. Understanding this form is essential because it defines the structure of the equation whose roots or solutions we seek.
Recommended video:
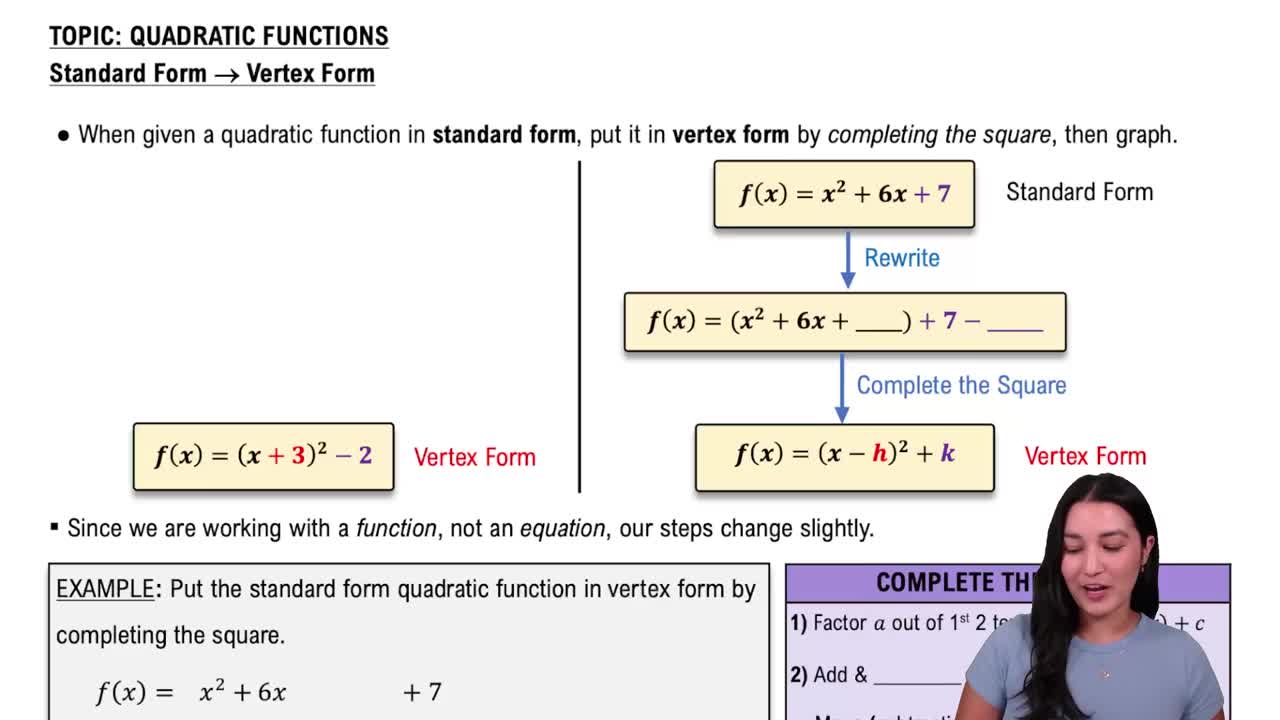
Converting Standard Form to Vertex Form
Zero-Factor Property
The zero-factor property states that if the product of two factors equals zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero. This property is used to find solutions of quadratic equations by factoring and setting each factor equal to zero.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Factoring Polynomials
Forming Quadratic Equations from Roots
Given the roots of a quadratic equation, you can reconstruct the equation by writing it as (x - root1)(x - root2) = 0 and then expanding. This reverse process helps find the coefficients a, b, and c based on the given solutions.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property

 6:12m
6:12mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
424
views
