In Exercises 57–64, find the vertical asymptotes, if any, the horizontal asymptote, if one exists, and the slant asymptote, if there is one, of the graph of each rational function. Then graph the rational function. g(x) = (4x^2 - 16x + 16)/(2x - 3)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Graphing Rational Functions
Problem 35
Textbook Question
Match the rational function in Column I with the appropriate description in Column II. Choices in Column II can be used only once. ƒ(x)=(x2+3x+4)/(x-5)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given rational function: \(f(x) = \frac{x^2 + 3x + 4}{x - 5}\).
Determine the domain by finding values of \(x\) that make the denominator zero. Set the denominator equal to zero: \(x - 5 = 0\).
Solve for \(x\) to find the excluded value from the domain: \(x = 5\). So, the domain is all real numbers except \(x = 5\).
Analyze the behavior of the function for asymptotes. Since the degree of the numerator (2) is greater than the degree of the denominator (1), there is an oblique (slant) asymptote.
Find the oblique asymptote by performing polynomial long division of \(x^2 + 3x + 4\) by \(x - 5\) to express \(f(x)\) as a polynomial plus a remainder over \(x - 5\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
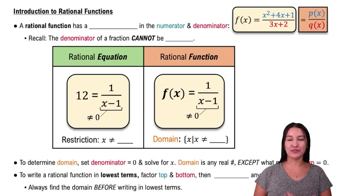
Rational Functions
A rational function is a ratio of two polynomials, expressed as f(x) = P(x)/Q(x), where Q(x) ≠ 0. Understanding the structure helps analyze its behavior, including domain restrictions and asymptotes.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rational Functions
Domain of a Rational Function
The domain consists of all real numbers except where the denominator equals zero, as division by zero is undefined. For f(x) = (x² + 3x + 4)/(x - 5), x ≠ 5 is excluded from the domain.
Recommended video:

Intro to Rational Functions
Asymptotes of Rational Functions
Asymptotes are lines that the graph approaches but never touches. Vertical asymptotes occur where the denominator is zero, and horizontal or oblique asymptotes depend on the degrees of numerator and denominator polynomials.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Asymptotes

 5:31m
5:31mWatch next
Master Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
531
views
