Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 129
Textbook Question
Perform the indicated operations and/or simplify each expression. Assume all variables represent positive real numbers. ∛2/3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the expression given: the cube root of the fraction \( \frac{2}{3} \), which can be written as \( \sqrt[3]{\frac{2}{3}} \).
Recall the property of radicals that allows you to separate the cube root of a fraction into the cube root of the numerator divided by the cube root of the denominator: \( \sqrt[3]{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt[3]{a}}{\sqrt[3]{b}} \).
Apply this property to rewrite the expression as \( \frac{\sqrt[3]{2}}{\sqrt[3]{3}} \).
Since the problem asks to simplify, consider rationalizing the denominator by multiplying numerator and denominator by \( \sqrt[3]{3^2} = \sqrt[3]{9} \) to eliminate the cube root in the denominator.
Perform the multiplication: \( \frac{\sqrt[3]{2} \times \sqrt[3]{9}}{\sqrt[3]{3} \times \sqrt[3]{9}} = \frac{\sqrt[3]{18}}{\sqrt[3]{27}} \), and then simplify the denominator \( \sqrt[3]{27} \) since 27 is a perfect cube.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cube Roots
A cube root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, gives the original number. For example, ∛8 = 2 because 2³ = 8. Understanding cube roots helps simplify expressions involving radicals with an index of 3.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Radical Expressions and Simplification
Radical expressions involve roots such as square roots or cube roots. Simplifying these expressions means rewriting them in the simplest form, often by factoring the radicand or rationalizing denominators, to make calculations easier and expressions clearer.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Radical Expressions with Fractions
Properties of Exponents and Radicals
Radicals can be expressed using fractional exponents, where the nth root of a number is the same as raising it to the 1/n power. For example, ∛(2/3) = (2/3)^(1/3). Using exponent rules helps in performing operations and simplifying radical expressions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
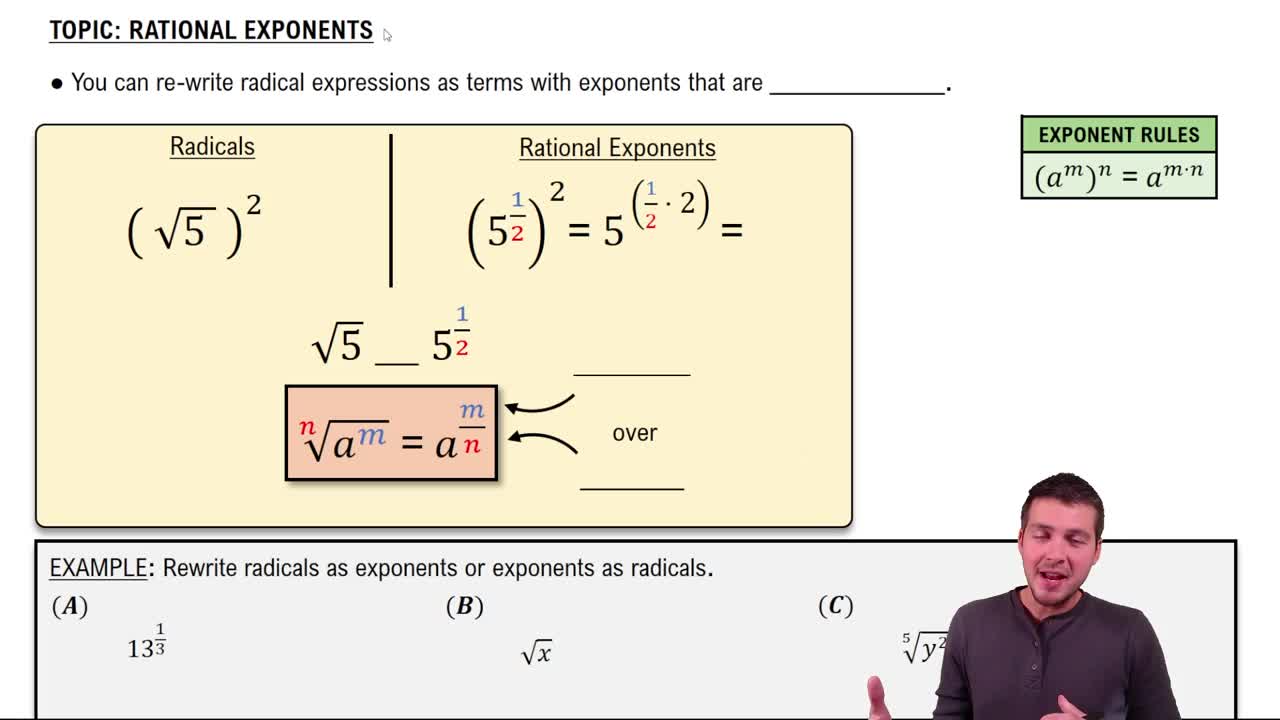
Rational Exponents
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
_If x=−2, then √x⁶ = x³.
583
views


