Solve each inequality in Exercises 65–70 and graph the solution set on a real number line.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Inequalities
Problem 74
Textbook Question
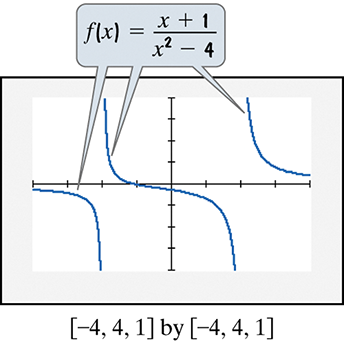
In Exercises 73–74, use the graph of the rational function to solve each inequality.
1/4(x + 2) > - 3/4(x - 2)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by rewriting the inequality \(\frac{1}{4}(x + 2) > -\frac{3}{4}(x - 2)\) to have all terms on one side for easier manipulation.
Multiply both sides of the inequality by 4 to eliminate the denominators, resulting in \(x + 2 > -3(x - 2)\).
Distribute the \(-3\) on the right side to get \(x + 2 > -3x + 6\).
Add \$3x\( to both sides and subtract 2 from both sides to isolate \)x\( terms on one side: \)x + 3x > 6 - 2\( which simplifies to \)4x > 4$.
Divide both sides by 4 to solve for \(x\), giving \(x > 1\). This is the solution to the inequality.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
7mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions and Their Graphs
A rational function is a ratio of two polynomials, expressed as f(x) = P(x)/Q(x). Its graph can have vertical asymptotes where the denominator is zero and horizontal or oblique asymptotes depending on the degrees of numerator and denominator. Understanding these features helps analyze the behavior of the function and solve inequalities involving it.
Recommended video:
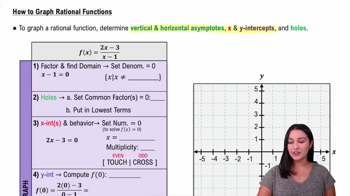
How to Graph Rational Functions
Solving Inequalities Involving Rational Expressions
To solve inequalities with rational expressions, first bring all terms to one side to form a single rational expression. Then determine where the numerator and denominator are zero to find critical points. Use these points to test intervals on the number line to see where the inequality holds true.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rationalizing Denominators
Interpreting Graphs to Solve Inequalities
Graphs of rational functions show where the function is positive or negative by its position relative to the x-axis. Points where the graph crosses or touches the x-axis correspond to zeros of the numerator. Vertical asymptotes indicate values excluded from the domain. Using the graph, one can visually identify solution intervals for inequalities.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Linear Inequalities
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
429
views


