Solve each equation using the quadratic formula. x2 = 2x - 5
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Square Root Property
Problem 47
Textbook Question
Height of a Projected Ball An astronaut on the moon throws a baseball upward. The astronaut is 6 ft, 6 in. tall, and the initial velocity of the ball is 30 ft per sec. The height s of the ball in feet is given by the equations=-2.7t2+30t+6.5,where t is the number of seconds after the ball was thrown. (a) After how many seconds is the ball 12 ft above the moon's surface? Round to the nearest hundredth. (b) How many seconds will it take for the ball to hit the moon's surface? Round to the nearest hundredth.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given height function of the ball: \(s(t) = -2.7t^2 + 30t + 6.5\), where \(s(t)\) is the height in feet and \(t\) is the time in seconds.
For part (a), set the height equal to 12 feet to find when the ball is 12 ft above the surface: \(-2.7t^2 + 30t + 6.5 = 12\).
Rearrange the equation to standard quadratic form: \(-2.7t^2 + 30t + 6.5 - 12 = 0\), which simplifies to \(-2.7t^2 + 30t - 5.5 = 0\).
Use the quadratic formula \(t = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\) with \(a = -2.7\), \(b = 30\), and \(c = -5.5\) to solve for \(t\). This will give two possible times when the ball is at 12 ft.
For part (b), find when the ball hits the moon's surface by setting \(s(t) = 0\): \(-2.7t^2 + 30t + 6.5 = 0\). Use the quadratic formula again with \(a = -2.7\), \(b = 30\), and \(c = 6.5\) to solve for \(t\). Choose the positive root as the time when the ball hits the surface.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
7mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
A quadratic function is a polynomial of degree two, typically written as s = at^2 + bt + c. Its graph is a parabola, which can open upward or downward depending on the sign of 'a'. Understanding the shape and properties of parabolas helps in interpreting the motion of objects under constant acceleration, such as the height of a thrown ball over time.
Recommended video:
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Solving Quadratic Equations
To find specific values of time when the ball reaches a certain height, you solve quadratic equations by setting the height equal to that value. Methods include factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. Solutions may represent different times when the ball is at the same height during its ascent and descent.
Recommended video:
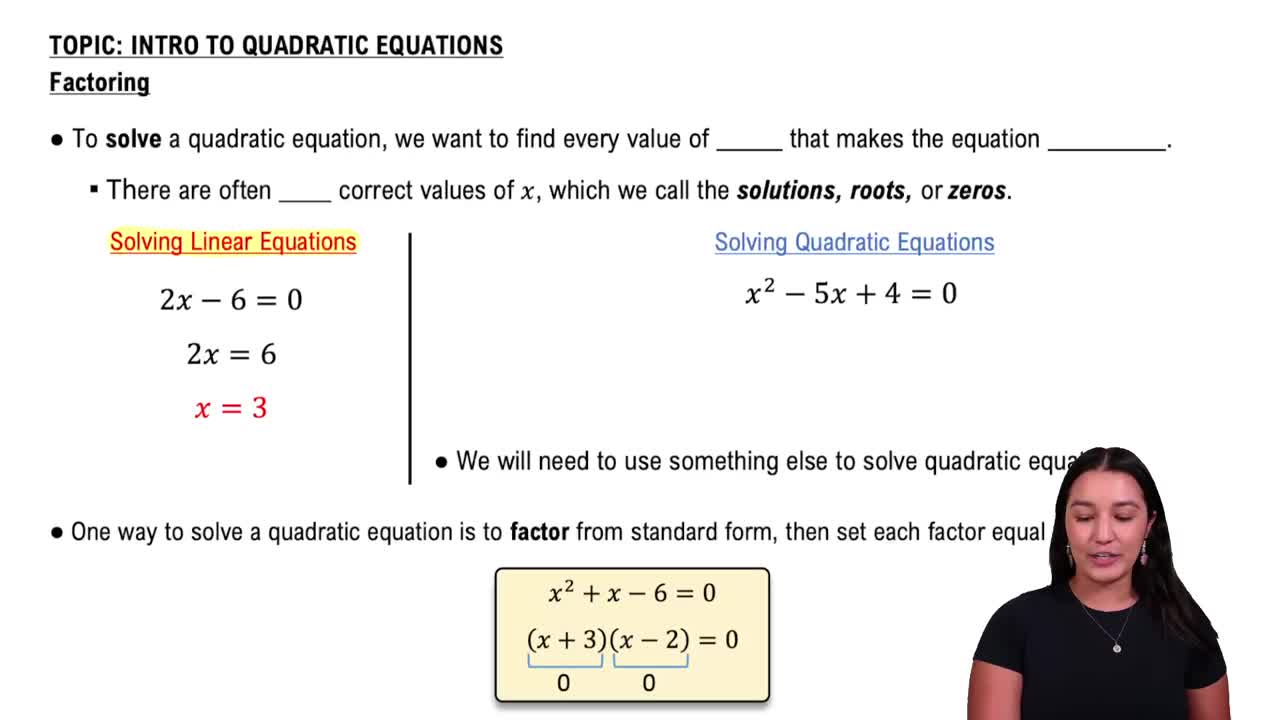
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Physical Interpretation of the Quadratic Model
The quadratic equation models the height of the ball considering initial velocity, gravity, and initial height. The coefficient of t^2 relates to gravitational acceleration on the moon, while the linear term represents initial velocity. Understanding this helps interpret results like when the ball reaches a certain height or returns to the surface.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula

 6:12m
6:12mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
717
views
