Determine the largest open intervals of the domain over which each function is (a) increasing. See Example 9.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Intro to Functions & Their Graphs
Problem 1
Textbook Question
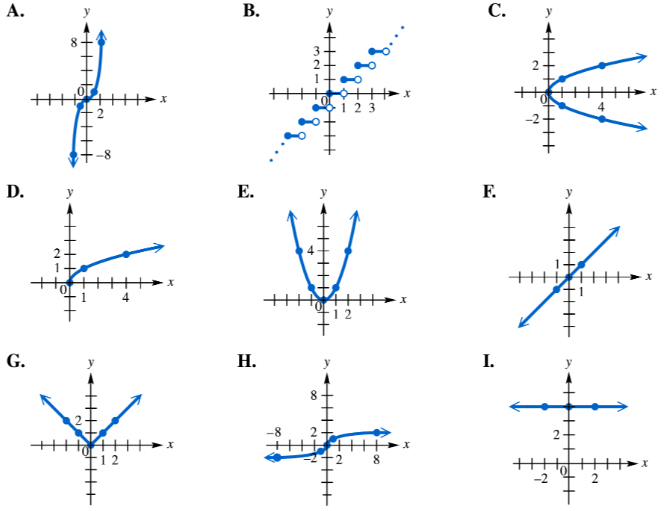
To answer each question, refer to the following basic graphs. Which one is the graph of ƒ(x)=x2? What is its domain?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the function given: ƒ(x) = x^2 is a quadratic function, which graphs as a parabola opening upwards.
Recall the shape of the graph of ƒ(x) = x^2: it is a U-shaped curve with its vertex at the origin (0,0).
Look at the provided basic graphs and select the one that matches this U-shaped parabola with vertex at the origin.
Determine the domain of ƒ(x) = x^2: since you can input any real number for x and get a real output, the domain is all real numbers.
Express the domain in interval notation as \((-\infty, \infty)\), meaning x can be any real number.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, typically written as f(x) = x². Its graph is a parabola that opens upwards, symmetric about the y-axis, with the vertex at the origin (0,0). Recognizing this shape helps identify the graph of f(x) = x².
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
Graph Interpretation
Graph interpretation involves analyzing the shape, position, and key features of a graph to match it with a given function. For f(x) = x², the graph is a U-shaped curve, and understanding these visual cues is essential to correctly identify the function's graph.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For f(x) = x², the domain is all real numbers since any real number can be squared without restriction.
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions

 5:2m
5:2mWatch next
Master Relations and Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
812
views
