Determine the largest open intervals of the domain over which each function is (c) constant. See Example 9.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Intro to Functions & Their Graphs
Problem 3
Textbook Question
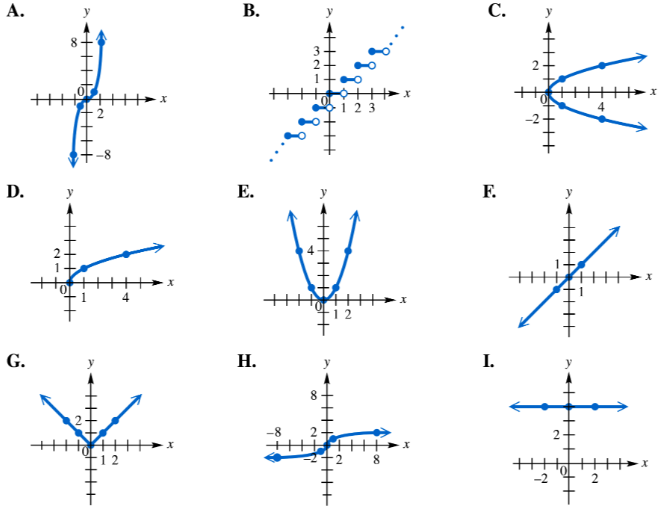
To answer each question, refer to the following basic graphs. Which one is the graph of ƒ(x)=x3? What is its range?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recall the basic shape of the graph of the function \(f(x) = x^{3}\). It is a cubic function, which typically has an S-shaped curve passing through the origin (0,0).
Identify the key characteristics of the cubic graph: it is symmetric about the origin (odd function), increases without bound as \(x\) goes to positive infinity, and decreases without bound as \(x\) goes to negative infinity.
Look at the given graphs and find the one that matches this description: an S-shaped curve passing through the origin, with the left side going down and the right side going up.
Once the correct graph is identified, determine the range of \(f(x) = x^{3}\). Since cubic functions can produce all real numbers as outputs, the range is all real numbers.
Express the range in interval notation as \((-\infty, \infty)\), indicating that the function's output values cover every real number.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cubic Function and Its Graph
A cubic function is a polynomial of degree three, typically written as f(x) = x³. Its graph is a smooth curve that passes through the origin, increasing from negative infinity to positive infinity, with an inflection point at (0,0). Recognizing this shape helps identify the correct graph among options.
Recommended video:
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Range of a Function
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values (f(x)) it can produce. For f(x) = x³, since x can be any real number and cubing preserves sign and magnitude, the range is all real numbers, meaning the graph extends infinitely in both vertical directions.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Interpreting Basic Graphs
Understanding how to read and interpret basic function graphs is essential. This includes identifying key features like intercepts, end behavior, and shape. For f(x) = x³, the graph’s characteristic S-shape and continuous increase help distinguish it from other polynomial graphs.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs & the Rectangular Coordinate System

 5:2m
5:2mWatch next
Master Relations and Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
563
views
