Graph the line passing through the given point and having the indicated slope. Plot two points on the line. through (3, -4), m = - 1/3
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Lines
Problem 66
Textbook Question
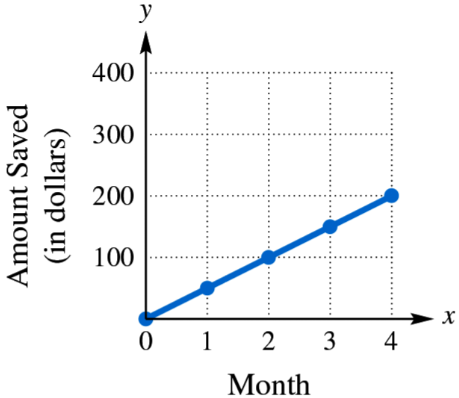
Find and interpret the average rate of change illustrated in each graph.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify two points on the graph to calculate the average rate of change. For example, use the points (2, 90) and (8, 360).
Step 2: Recall the formula for the average rate of change between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\):
\[\text{Average Rate of Change} = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}\]
Step 3: Substitute the coordinates of the chosen points into the formula:
\[\frac{360 - 90}{8 - 2}\]
Step 4: Simplify the expression to find the average rate of change, which represents the change in carbon production rate per year.
Step 5: Interpret the result as the average increase in Company X's bi-yearly carbon production rate (in tonnes) for each year over the 8-year period.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Average Rate of Change
The average rate of change measures how much a quantity changes, on average, between two points. It is calculated as the change in the output (y-values) divided by the change in the input (x-values). In this context, it shows how the carbon production rate changes per year.
Recommended video:

Change of Base Property
Interpreting Coordinates on a Graph
Each point on the graph represents a specific year and the corresponding carbon production rate. Understanding these coordinates helps in calculating the rate of change and interpreting real-world data, such as how production increases over time.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example
Linear Relationships
A linear relationship is shown by a straight line on the graph, indicating a constant rate of change. Here, the straight line connecting the points suggests that the carbon production rate increases steadily over the years.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
553
views


