If one point on a line is (2, −6) and the line's slope is -3/2, find the y-intercept.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Lines
Problem 21
Textbook Question
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−6, 4) and is perpendicular to the line that has an x intercept of 2 and a y-intercept of -4.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the slope of the given line using its intercepts. The line passes through the points (2, 0) and (0, -4). Use the slope formula: \(m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}\).
Calculate the slope of the given line by substituting the points: \(m = \frac{0 - (-4)}{2 - 0} = \frac{4}{2}\).
Determine the slope of the line perpendicular to the given line. Recall that perpendicular slopes are negative reciprocals, so if the original slope is \(m\), the perpendicular slope is \(-\frac{1}{m}\).
Use the point-slope form of a line equation with the perpendicular slope and the given point \((-6, 4)\): \(y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)\).
Rewrite the equation from the previous step into slope-intercept form \(y = mx + b\) by solving for \(y\) and simplifying.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Slope-Intercept Form of a Linear Equation
The slope-intercept form is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b is the y-intercept. This form makes it easy to identify the slope and where the line crosses the y-axis, which is essential for graphing and writing linear equations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
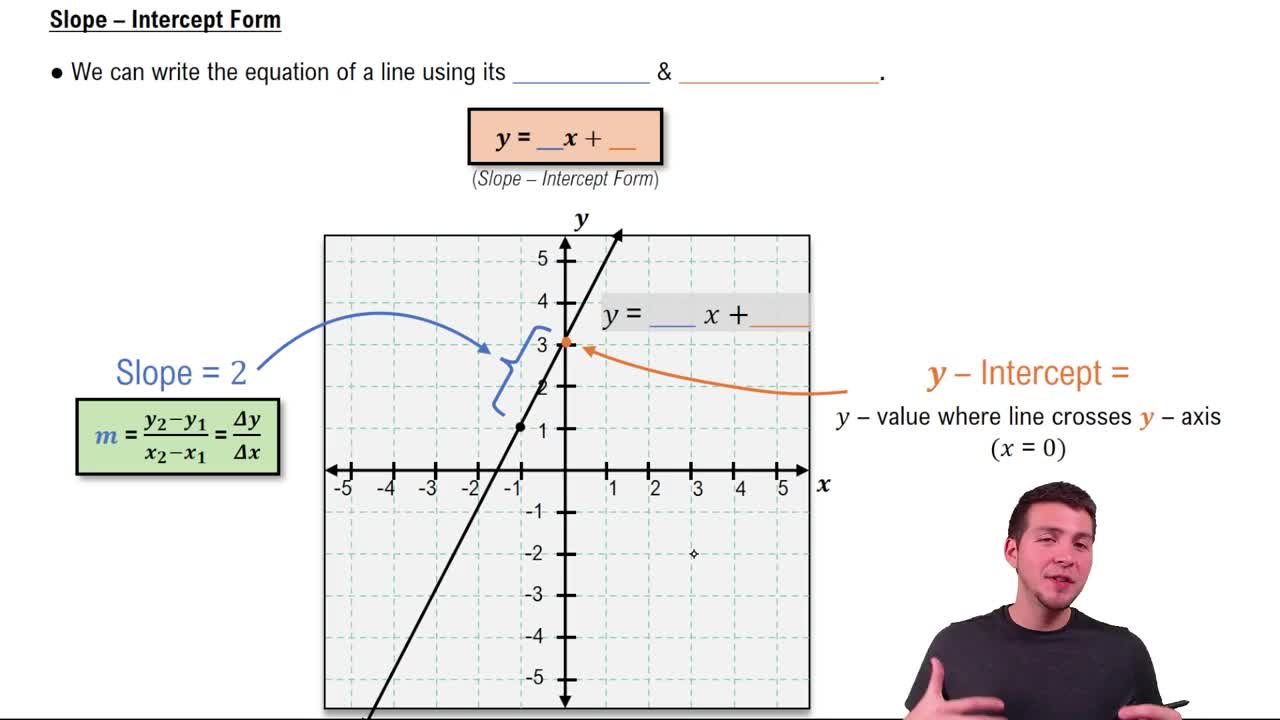
Slope-Intercept Form
Finding the Slope from Intercepts
A line's slope can be found using two points, such as the x- and y-intercepts. The slope m is calculated as the change in y divided by the change in x (m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)). Knowing the slope of the given line is necessary to find the slope of the perpendicular line.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Slope-Intercept Form
Perpendicular Lines and Their Slopes
Two lines are perpendicular if their slopes are negative reciprocals, meaning m1 * m2 = -1. If one line has slope m, the perpendicular line's slope is -1/m. This relationship helps determine the slope of the required line passing through a given point.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Parallel & Perpendicular Lines
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
44
views


