Let ƒ(x)=-3x+4 and g(x)=-x2+4x+1. Find each of the following. Simplify if necessary. ƒ(3t-2)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Graphs and Coordinates
Problem 80
Textbook Question
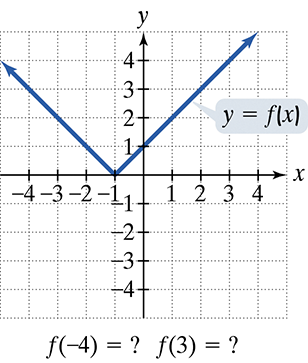
In Exercises 77–92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b.the x-intercepts, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph. 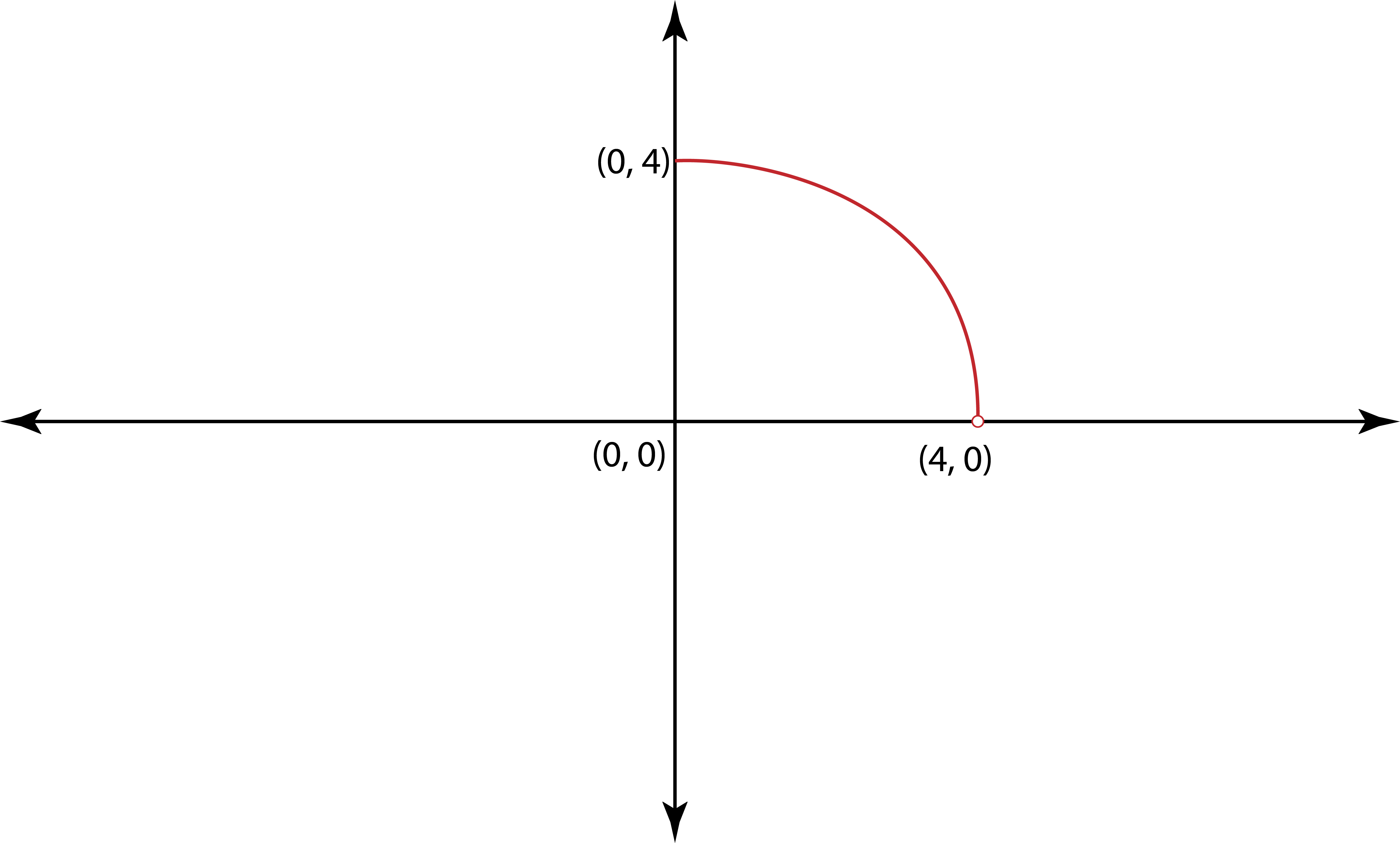
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: To determine the domain of the function, observe the x-values for which the function is defined. For the first graph, the function is defined from x = 0 to x = 4. For the second graph, the function is defined for all x-values.
Step 2: To find the x-intercepts, look for the points where the graph crosses the x-axis. For the first graph, the x-intercept is at (4, 0). For the second graph, the x-intercept is at (0, 0).
Step 3: To find the missing function values, locate the corresponding y-values for the given x-values on the graph. For the second graph, find the y-values for x = -4 and x = 3.
Step 4: For the second graph, when x = -4, trace vertically to the graph to find the y-value. Similarly, when x = 3, trace vertically to the graph to find the y-value.
Step 5: Summarize the findings: The domain, x-intercepts, and missing function values for each graph.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. Understanding the domain is crucial for determining where the function can be evaluated, which can be influenced by factors such as discontinuities or restrictions in the function's definition.
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
X-Intercepts
X-intercepts are the points where a function crosses the x-axis, meaning the output value (y) is zero at these points. To find x-intercepts, one typically sets the function equal to zero and solves for x. Identifying these points is essential for understanding the behavior of the function and its graphical representation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Intercepts
Function Values
Function values represent the output of a function for given input values. In the context of a graph, these values can be determined by evaluating the function at specific x-values. Missing function values, often indicated by question marks, require careful analysis of the graph to estimate or calculate the corresponding y-values.
Recommended video:

Function Composition

 5:10m
5:10mWatch next
Master Graphs & the Rectangular Coordinate System with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
721
views
