Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Graphs and Coordinates
Problem 86
Textbook Question
In Exercises 85–90, find the x-intercepts of the graph of each equation. Then use the x-intercepts to match the equation with its graph. [The graphs are labeled (a) through (f).]
a) b)
b)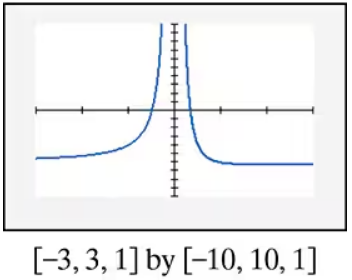 c)
c)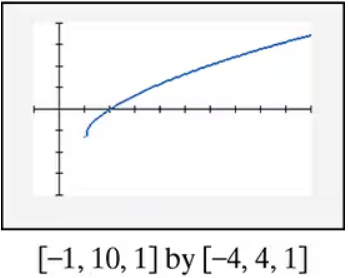 d)
d)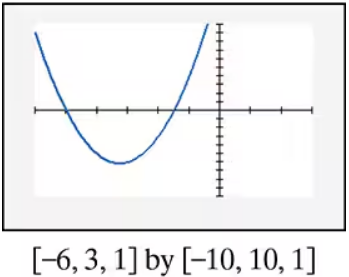 e)
e)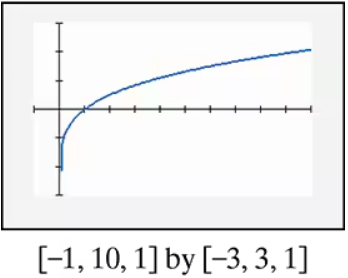 f)
f) 
y=x−4+x+4−4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
To find the x-intercepts of the graph, set the equation equal to zero because x-intercepts occur where the graph crosses the x-axis, meaning \(y = 0\). So, start with the equation: \$0 = \sqrt{\,x - 4\,} + \sqrt{\,x + 4\,} - 4$.
Isolate the square root terms on one side to simplify the equation. Add 4 to both sides to get: \$4 = \sqrt{\,x - 4\,} + \sqrt{\,x + 4\,}$.
To eliminate the square roots, consider squaring both sides of the equation. Remember, when squaring, use the formula \((a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2\). So, square both sides: \$4^2 = (\sqrt{\,x - 4\,} + \sqrt{\,x + 4\,})^2$.
Expand the right side using the formula: \$16 = (x - 4) + 2\sqrt{(x - 4)(x + 4)} + (x + 4)\(. Simplify the terms without the square root: \)16 = 2x + 2\sqrt{(x - 4)(x + 4)}$.
Isolate the square root term: \$16 - 2x = 2\sqrt{(x - 4)(x + 4)}\(. Then divide both sides by 2: \)\frac{16 - 2x}{2} = \sqrt{(x - 4)(x + 4)}\(. This simplifies to \)8 - x = \sqrt{x^2 - 16}\(. Next, square both sides again to eliminate the square root and solve for \)x$.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Finding x-intercepts
X-intercepts are points where the graph crosses the x-axis, meaning the y-value is zero. To find them, set y = 0 in the equation and solve for x. This helps identify key points that characterize the graph's shape and position.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Intercepts
Domain of Radical Functions
For functions involving square roots, the expression inside the root must be non-negative to yield real values. Determining the domain involves solving inequalities like x - 4 ≥ 0 and x + 4 ≥ 0, which restricts the possible x-values and affects where the graph exists.
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Graph Matching Using Intercepts
Matching equations to graphs often relies on key features like intercepts and domain restrictions. By finding x-intercepts and understanding the domain, you can compare these points and intervals to the given graphs to identify the correct match.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Intercepts

 5:10m
5:10mWatch next
Master Graphs & the Rectangular Coordinate System with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
In Exercises 77–92, use the graph to determine a. the function's domain; b.the x-intercepts, if any; and e. the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.
944
views
