Graph each inequality. y≥x2−9
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Graphing Systems of Inequalities
Problem 31
Textbook Question
Graph the solution set of each system of inequalities or indicate that the system has no solution.
{y>2x−3y<−x+6
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the two inequalities in the system: \(y > 4x - 2\) and \(y < -3x + 9\).
Graph the boundary lines for each inequality: the line \(y = 4x - 2\) and the line \(y = -3x + 9\). Use a solid line if the inequality includes equality (≥ or ≤), but here use dashed lines because the inequalities are strict ( > and < ).
Determine the shading for each inequality: For \(y > 4x - 2\), shade the region above the line \(y = 4x - 2\). For \(y < -3x + 9\), shade the region below the line \(y = -3x + 9\).
Find the intersection of the two shaded regions. This overlapping area represents the solution set to the system of inequalities.
If the shaded regions do not overlap, then the system has no solution. Otherwise, the solution set is the region where both inequalities are true simultaneously.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Graphing Linear Inequalities
Graphing linear inequalities involves plotting the boundary line given by the corresponding linear equation and then shading the region that satisfies the inequality. For strict inequalities (>, <), the boundary line is dashed to indicate points on the line are not included. The shaded area represents all solutions that make the inequality true.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
System of Inequalities
A system of inequalities consists of two or more inequalities considered simultaneously. The solution set is the intersection of the individual solution regions, meaning only points that satisfy all inequalities are included. If no common region exists, the system has no solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Systems of Inequalities
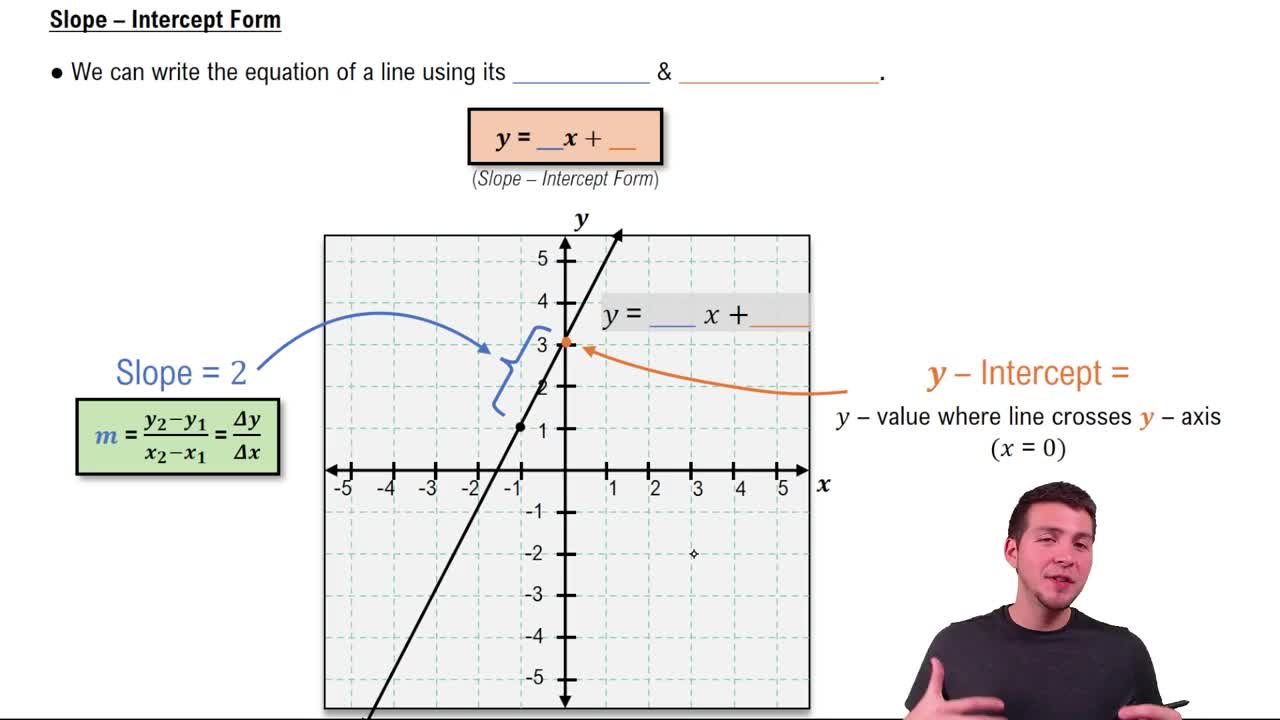
Slope-Intercept Form and Interpretation
The slope-intercept form y = mx + b expresses a line where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Understanding the slope helps determine the line's direction, while the intercept shows where it crosses the y-axis. This form is essential for quickly graphing the boundary lines of inequalities.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Slope-Intercept Form
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
439
views


