The functions in Exercises 93–95 are all one-to-one. For each function, (a) find an equation for f^(-1)x, the inverse function. (b) Verify that your equation is correct by showing that f(f^(-1)(x)) = x and f^(-1)(f(x)) = x. f(x) = (x - 7)/(x + 2)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Function Composition
Problem 79
Textbook Question
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
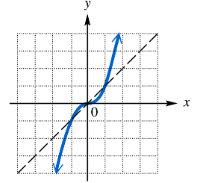
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand that the inverse of a function reflects the graph of the original function across the line \(y = x\). This means every point \((a, b)\) on the original function will correspond to a point \((b, a)\) on the inverse function.
Step 2: Identify key points on the original graph. For example, note points where the curve crosses grid lines or has notable coordinates, such as the origin \((0,0)\) and other points where the function value is clear.
Step 3: For each key point \((x, y)\) on the original graph, plot the point \((y, x)\) on the coordinate plane. This will give you points on the inverse function.
Step 4: Connect these new points smoothly, maintaining the shape but reflected over the line \(y = x\). The inverse graph should be a mirror image of the original graph with respect to this line.
Step 5: Optionally, draw the line \(y = x\) as a reference to verify that the original function and its inverse are symmetric about this line.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
One-to-One Function
A one-to-one function is a function where each input corresponds to a unique output, and no two different inputs share the same output. This property ensures the function has an inverse because it can be reversed without ambiguity.
Recommended video:

Decomposition of Functions
Inverse Function
The inverse of a function reverses the roles of inputs and outputs, swapping x and y values. Graphically, the inverse function is the reflection of the original function across the line y = x, meaning every point (a, b) on the function corresponds to (b, a) on its inverse.
Recommended video:

Graphing Logarithmic Functions
Graphing and Reflection Across y = x
To graph the inverse of a function, reflect the original graph across the line y = x. This means that the x-coordinates and y-coordinates of all points on the original graph are interchanged, producing the graph of the inverse function.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Shifted & Reflected Functions

 4:56m
4:56mWatch next
Master Function Composition with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
593
views
