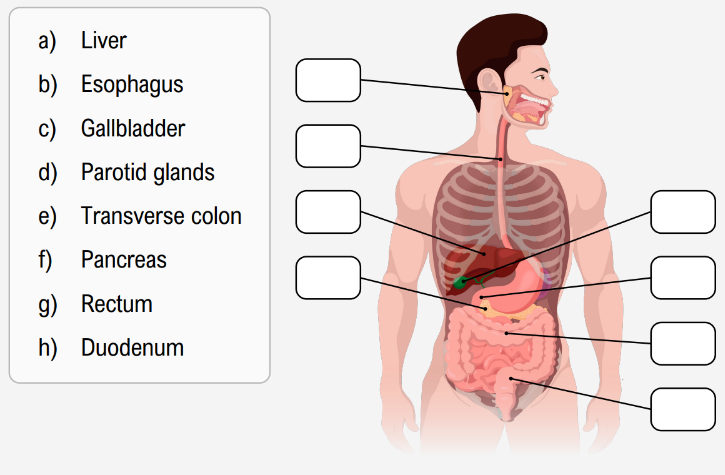
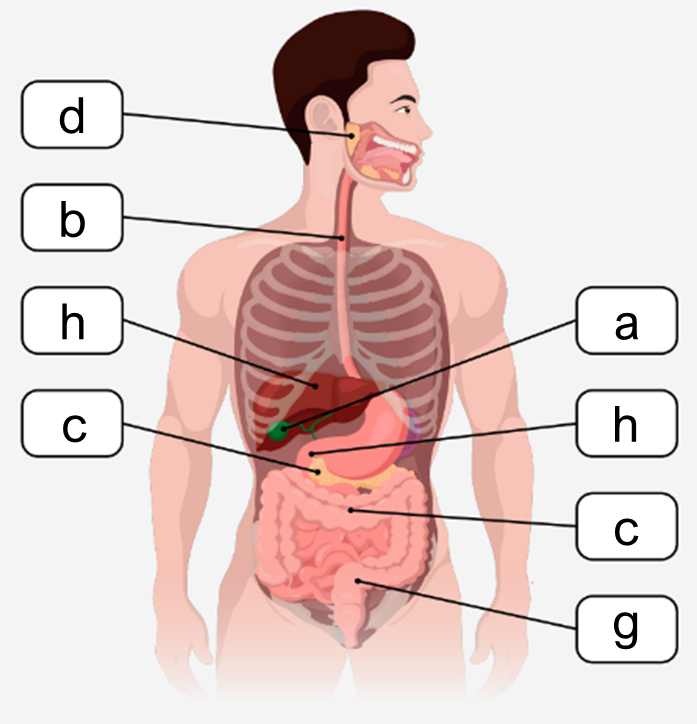
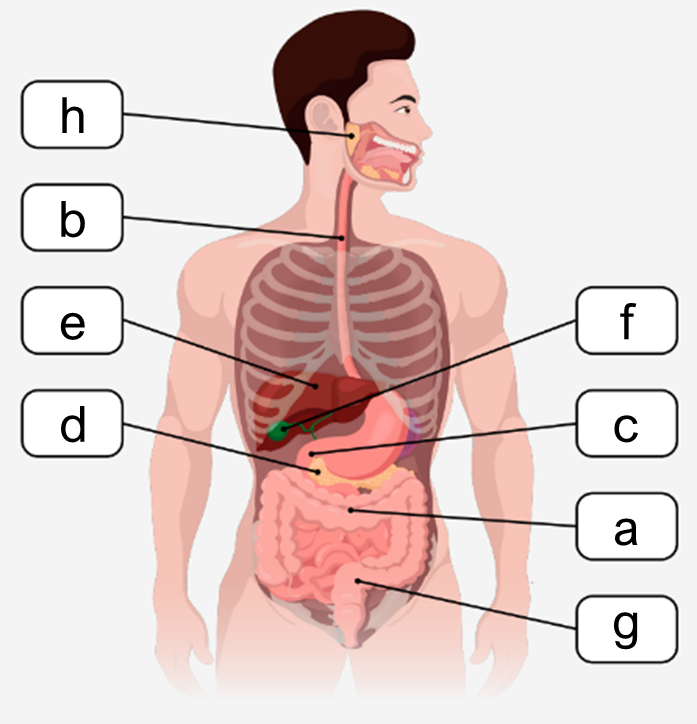
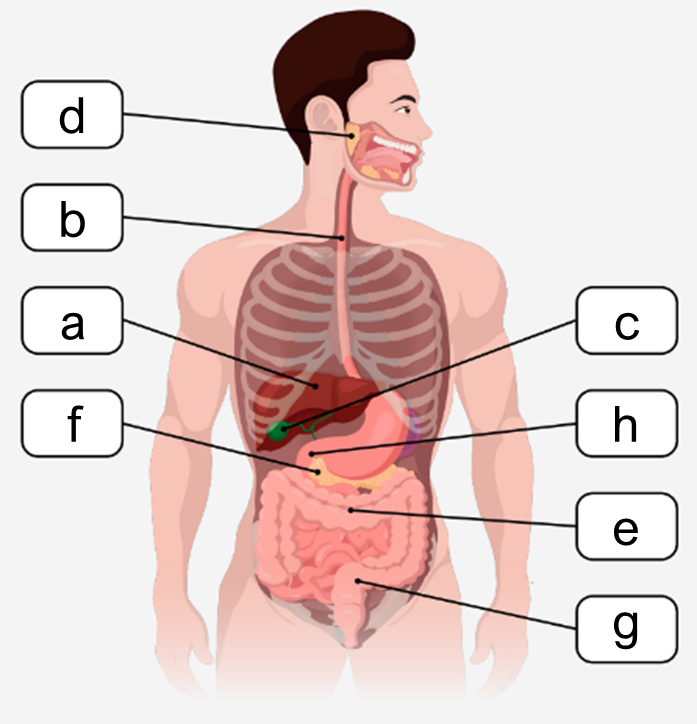
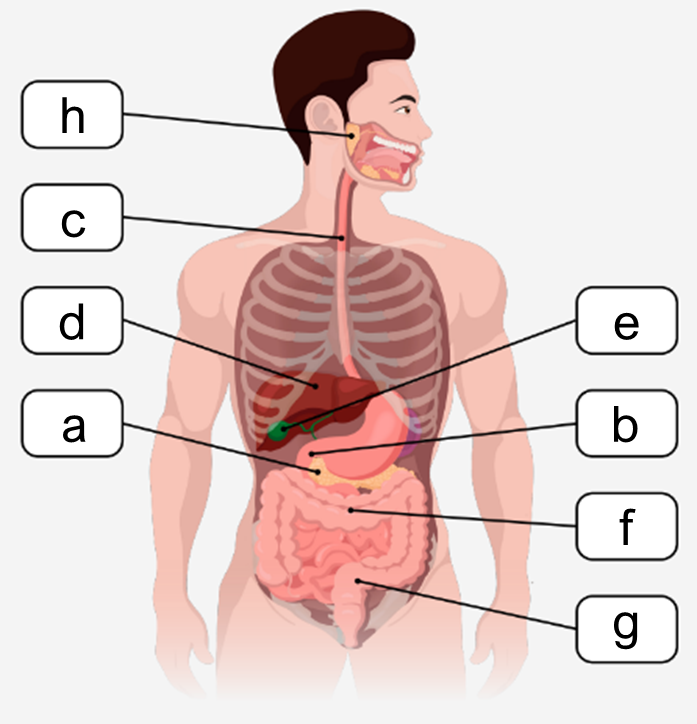
The digestive system plays a crucial role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating solid waste. It is organized into two main groups of organs: the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. The alimentary canal, also known as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is a continuous muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the anus. This canal includes the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, and large intestines, each contributing to different stages of digestion.
The oral cavity initiates digestion by mechanically breaking down food, while the pharynx and esophagus serve as passageways for food to reach the stomach. The stomach is a key site for acidic and enzymatic digestion, where food is further broken down by gastric juices. The small intestines are essential for enzymatic digestion and nutrient absorption; damage or bypassing this section can significantly impair nutrient uptake. The large intestines primarily focus on water reabsorption and the elimination of waste as solid feces.
Accessory organs, although not part of the alimentary canal, support digestion by producing and storing substances necessary for breaking down food. These include the teeth and tongue, which aid in mechanical digestion and food manipulation. The salivary glands secrete saliva to moisten and lubricate food, facilitating swallowing and initial chemical digestion. The liver produces bile, a substance critical for emulsifying fats, enhancing their digestion. Bile is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder until needed. The pancreas contributes by secreting digestive enzymes and buffers that neutralize stomach acid, ensuring optimal conditions for enzymatic activity in the small intestines.
Understanding the division between the alimentary canal and accessory organs helps clarify the digestive system's organization and function. This system efficiently transforms food into absorbable nutrients while managing waste elimination, highlighting the importance of each organ's role in maintaining overall digestive health.