Graph: f(x) = -2(x − 1)² (x + 3).
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 90
Textbook Question
Solve each problem. A comprehensive graph of ƒ(x)=x4-7x3+18x2-22x+12 is shown in the two screens, along with displays of the two real zeros. Find the two remaining nonreal complex zeros.
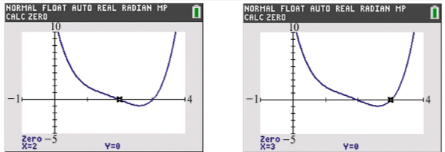
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given polynomial function: \(f(x) = x^4 - 7x^3 + 18x^2 - 22x + 12\).
Since the problem states there are two real zeros already found, use these real zeros to factor the polynomial partially. Express \(f(x)\) as the product of \((x - r_1)(x - r_2)\) and a quadratic polynomial, where \(r_1\) and \(r_2\) are the real zeros.
Perform polynomial division or synthetic division to divide \(f(x)\) by the quadratic factor formed from the two real zeros, resulting in a quadratic polynomial \(q(x)\).
Set the quadratic polynomial \(q(x)\) equal to zero: \(q(x) = 0\), and prepare to solve for the remaining zeros.
Use the quadratic formula \(x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\) on \(q(x)\) to find the two nonreal complex zeros, noting that the discriminant will be negative, indicating complex roots.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
7mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra states that a polynomial of degree n has exactly n roots in the complex number system, counting multiplicities. For a quartic polynomial like ƒ(x), there are four zeros total, which can be real or complex. Understanding this helps in knowing that after finding the real zeros, the remaining zeros must be complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Algebraic Expressions
Polynomial Division and Factoring
Once the real zeros are known, polynomial division (such as synthetic or long division) is used to divide the original polynomial by the factors corresponding to these zeros. This reduces the polynomial to a quadratic, which can then be analyzed to find the remaining zeros. Factoring simplifies the problem and isolates the complex roots.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Factoring Polynomials
Complex Zeros and the Quadratic Formula
When the reduced polynomial is quadratic and does not factor nicely over the reals, the quadratic formula is used to find its roots. If the discriminant is negative, the solutions are complex conjugates. This concept is essential to identify and express the nonreal complex zeros of the polynomial.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
10
views
