See Exercise 47. (b)Which equation has two nonreal complex solutions?
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Square Root Property
Problem 2
Textbook Question
Match the equation in Column I with its solution(s) in Column II. x2 = -25
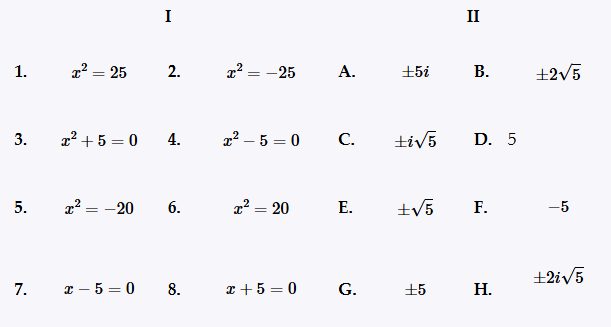
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recognize that the equation given is \(x^2 = -25\), which is a quadratic equation where the square of \(x\) equals a negative number.
Recall that in the set of real numbers, the square of any real number is always non-negative, so \(x^2 = -25\) has no real solutions.
To find solutions, consider the complex number system where \(i\) is defined as the imaginary unit with the property \(i^2 = -1\).
Rewrite the equation as \(x^2 = -25 = 25 \times (-1) = 25i^2\), then take the square root of both sides to get \(x = \pm \sqrt{25i^2}\).
Simplify the square root to \(x = \pm 5i\), which are the two complex solutions to the equation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solving Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations are polynomial equations of degree two, typically in the form ax² + bx + c = 0. Solving them involves finding values of x that satisfy the equation, often using factoring, completing the square, or the quadratic formula.
Recommended video:
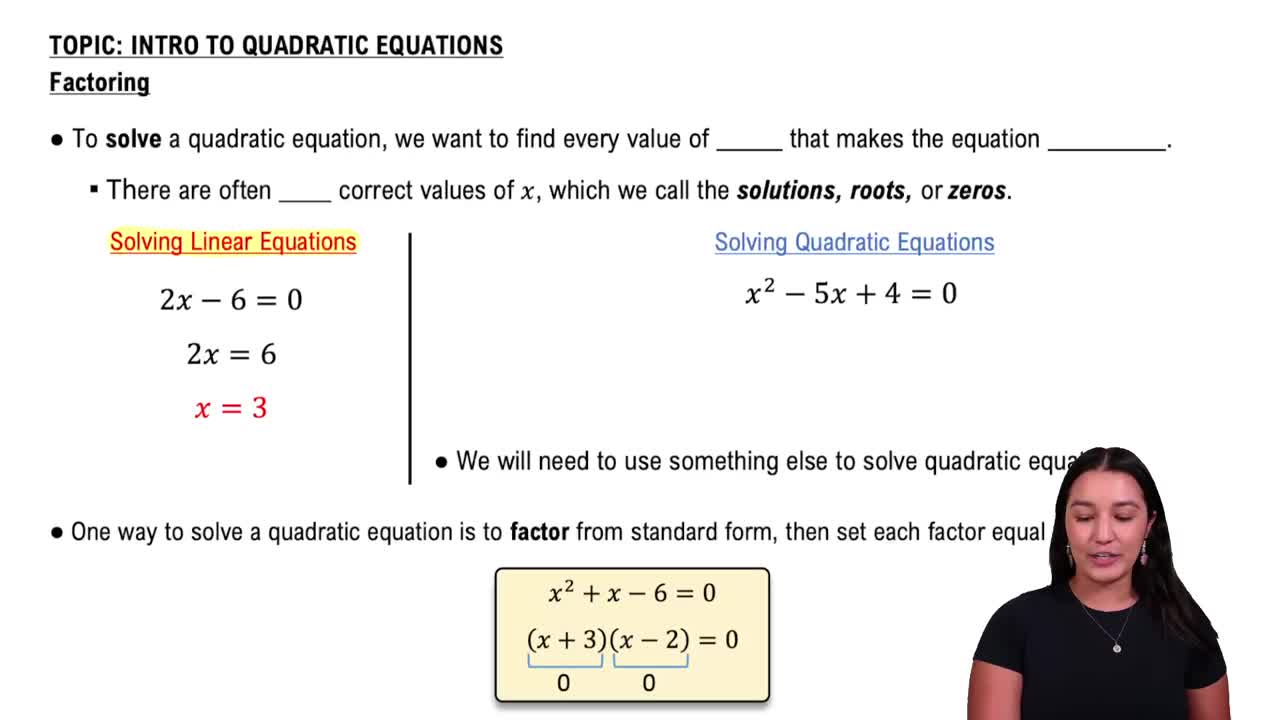
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Complex Numbers and Imaginary Unit
When a quadratic equation has no real solutions, such as x² = -25, solutions involve complex numbers. The imaginary unit i is defined as √-1, allowing expressions like √-25 to be written as 5i, representing imaginary solutions.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Complex Numbers
Square Roots of Negative Numbers
Taking the square root of a negative number is not possible within the real numbers. Instead, it introduces imaginary numbers, where √-a = i√a for a > 0. This concept is essential for understanding solutions to equations like x² = -25.
Recommended video:

Square Roots of Negative Numbers

 6:12m
6:12mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
698
views
