Dimensions of a Right Triangle The shortest side of a right triangle is 7 in. shorter than the middle side, while the longest side (the hypotenuse) is 1 in. longer than the middle side. Find the lengths of the sides.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Square Root Property
Problem 47
Textbook Question
Which equation has two real, distinct solutions? Do not actually solve.
A. (3x-4)² = -9 B. (4-7x)² = 0 C. (5x-9)(5x-9) = 0 D. (7x+4)² = 11
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recall that an equation of the form \( (ax + b)^2 = c \) will have two real, distinct solutions if and only if \( c > 0 \). This is because taking the square root of both sides yields two different values, \( \sqrt{c} \) and \( -\sqrt{c} \), when \( c \) is positive.
Analyze option A: \( (3x - 4)^2 = -9 \). Since the right side is negative, \( -9 < 0 \), there are no real solutions because a square cannot equal a negative number in the real number system.
Analyze option B: \( (4 - 7x)^2 = 0 \). Here, \( c = 0 \), so there is exactly one real solution (a repeated root), not two distinct solutions.
Analyze option C: \( (5x - 9)(5x - 9) = 0 \) is equivalent to \( (5x - 9)^2 = 0 \), which again means \( c = 0 \) and only one real solution (a repeated root).
Analyze option D: \( (7x + 4)^2 = 11 \). Since \( 11 > 0 \), this equation will have two real, distinct solutions because the square root of 11 is positive and negative, giving two different values for \( x \).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Discriminant and Nature of Solutions
The discriminant of a quadratic equation determines the number and type of solutions. If the discriminant is positive, there are two distinct real solutions; if zero, one real repeated solution; if negative, no real solutions. Understanding this helps identify equations with two real, distinct roots without solving.
Recommended video:

The Discriminant
Square of a Binomial and Its Properties
Expressions like (ax + b)² represent a perfect square trinomial, which equals zero only when the binomial itself is zero, leading to one repeated root. Recognizing this form helps determine if an equation has one or multiple solutions without expanding or solving.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Solving Quadratic Equations by Inspection
Some quadratic equations can be analyzed by examining their structure, such as whether the squared term equals a positive, zero, or negative number. This approach allows quick assessment of the number and type of solutions based on the equation's form, avoiding full algebraic solving.
Recommended video:
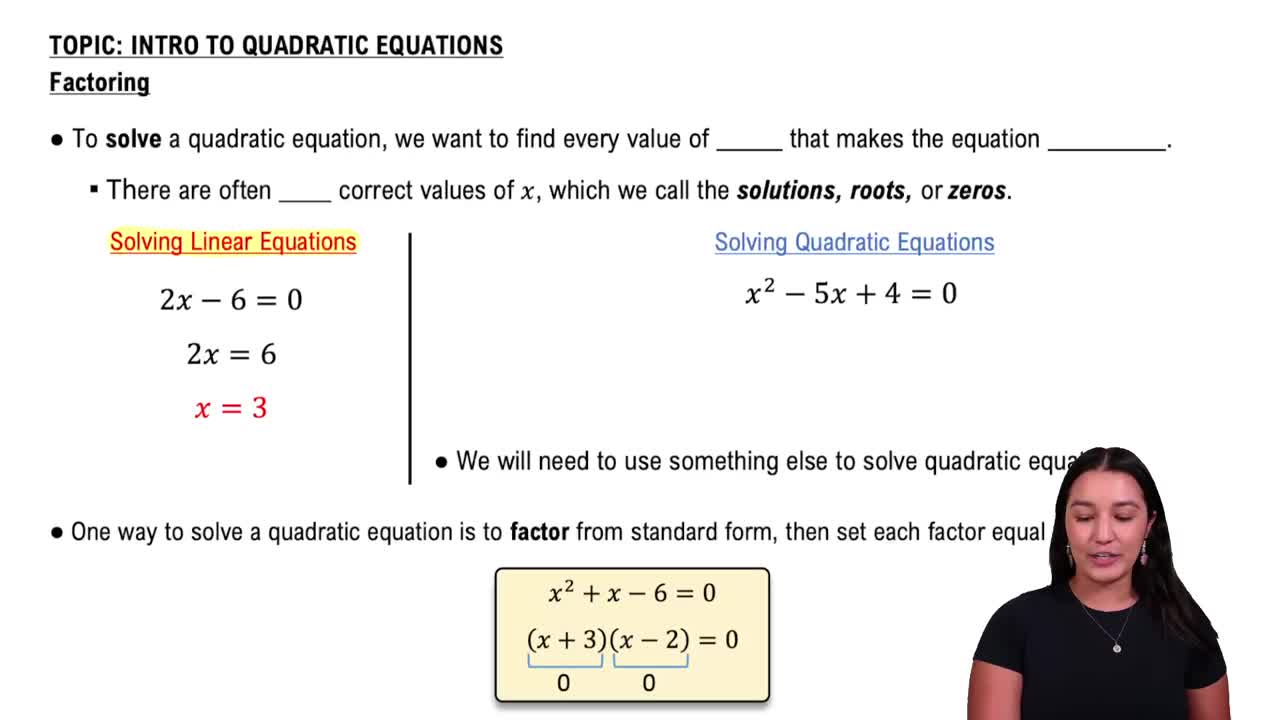
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring

 6:12m
6:12mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
537
views
