Textbook Question
Follow the seven steps to graph each rational function. f(x)=2x2/(x2−1)
7
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
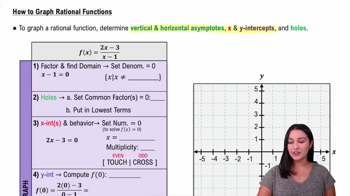


 5:31m
5:31mMaster Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning