Determine the following limits at infinity.
lim x→−∞ 3x^11
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
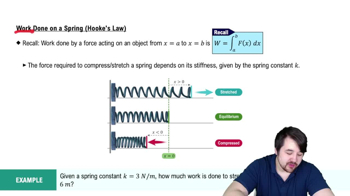
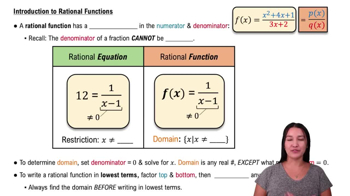

 6:47m
6:47mMaster Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning