Look again at the region R in Figure 6.38 (p. 439). Explain why it would be difficult to use the washer method to find the volume of the solid of revolution that results when R is revolved about the y-axis.
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
9. Graphical Applications of Integrals
Introduction to Volume & Disk Method
Problem 6.3.74a
Textbook Question
Consider the region R in the first quadrant bounded by y=x^1/n and y=x^n, where n>1 is a positive number.
a. Find the volume V(n) of the solid generated when R is revolved about the x-axis. Express your answer in terms of n.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the region R bounded by the curves \(y = x^{\frac{1}{n}}\) and \(y = x^n\) in the first quadrant. Since \(n > 1\), these two curves intersect at \(x=0\) and \(x=1\) because \(x^{\frac{1}{n}} = x^n\) implies \(x=0\) or \(x=1\).
Set up the volume integral using the method of washers (disks with holes) when revolving around the x-axis. The volume \(V(n)\) is given by integrating the difference of the squares of the outer and inner radii:
\[V(n) = \pi \int_0^1 \left[ (\text{outer radius})^2 - (\text{inner radius})^2 \right] \, dx.\]
Determine which curve is the outer radius and which is the inner radius with respect to the x-axis. Since \(y = x^{\frac{1}{n}}\) is greater than \(y = x^n\) on \((0,1)\) for \(n > 1\), the outer radius is \(x^{\frac{1}{n}}\) and the inner radius is \(x^n\).
Write the integral explicitly as: \[V(n) = \pi \int_0^1 \left[ (x^{\frac{1}{n}})^2 - (x^n)^2 \right] \, dx = \pi \int_0^1 \left( x^{\frac{2}{n}} - x^{2n} \right) \, dx.\] Then, integrate term-by-term using the power rule for integrals.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
8mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Defining the Region Bounded by Curves
Understanding the region R requires identifying the curves y = x^(1/n) and y = x^n and their intersection points in the first quadrant. Since n > 1, these functions define a closed area between them for x in [0,1]. Recognizing the limits of integration is essential for setting up the volume integral.
Recommended video:
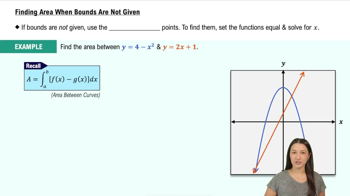
Finding Area When Bounds Are Not Given
Volume of Solids of Revolution Using the Disk/Washer Method
When a region is revolved about the x-axis, the volume can be found by integrating the area of circular cross-sections perpendicular to the axis. The washer method applies when there is an inner and outer radius, calculated from the bounding curves, and the volume is the integral of π(outer radius² - inner radius²) dx over the interval.
Recommended video:
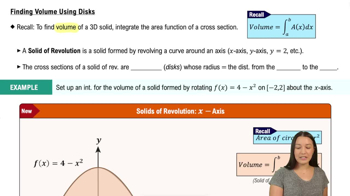
Finding Volume Using Disks
Integration of Power Functions
The volume integral involves integrating expressions like x^(2/n) and x^(2n), which are power functions. Applying the power rule for integration, ∫x^m dx = x^(m+1)/(m+1), is necessary to find a closed-form expression for V(n) in terms of n.
Recommended video:

Representing Functions as Power Series

 5:38m
5:38mWatch next
Master Introduction to Cross Sections with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
17
views
