Evaluate cos (11π/12) as cos (π/4 + 2π/3).
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
0. Functions
Trigonometric Identities
Problem 1.3.54
Textbook Question
Solving Trigonometric Equations
For Exercises 51–54, solve for the angle θ, where 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π.
sin² θ = cos² θ
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by recognizing the given equation: sin² θ = cos² θ. This can be rewritten using the identity sin² θ + cos² θ = 1.
Rearrange the identity to express one trigonometric function in terms of the other: sin² θ = 1 - cos² θ.
Substitute this expression into the original equation: 1 - cos² θ = cos² θ.
Combine like terms to form a single equation: 1 = 2cos² θ.
Solve for cos² θ by dividing both sides by 2, then take the square root to find the possible values of cos θ. Consider the range 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π to determine the specific angles that satisfy the equation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric identities are equations that involve trigonometric functions and are true for all values of the variables involved. A key identity relevant to the given equation is the Pythagorean identity, which states that sin² θ + cos² θ = 1. Understanding these identities is crucial for simplifying and solving trigonometric equations.
Recommended video:
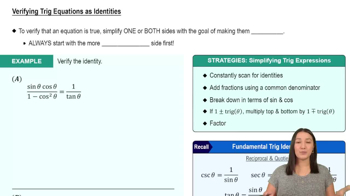
Verifying Trig Equations as Identities
Solving Trigonometric Equations
Solving trigonometric equations involves finding the angles that satisfy the equation within a specified interval. In this case, we need to manipulate the equation sin² θ = cos² θ to find the values of θ between 0 and 2π. Techniques often include using identities, factoring, and applying inverse trigonometric functions.
Recommended video:
Solving Logarithmic Equations
Unit Circle
The unit circle is a fundamental concept in trigonometry that provides a geometric interpretation of the sine and cosine functions. It is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. Understanding the unit circle helps in determining the angles corresponding to specific sine and cosine values, which is essential for solving the equation sin² θ = cos² θ.
Recommended video:
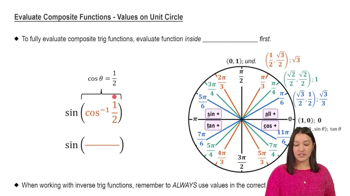
Evaluate Composite Functions - Values on Unit Circle
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
170
views


