Mean Value Theorem and graphs Find all points on the interval (1,3) at which the slope of the tangent line equals the average rate of change of f on [1,3]. Reconcile your results with the Mean Value Theorem. <IMAGE>
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives
Curve Sketching
Problem 4.4.15
Textbook Question
Graphing functions Use the guidelines of this section to make a complete graph of f.
f(x) = x² - 6x
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of function: The function f(x) = x² - 6x is a quadratic function, which means its graph will be a parabola.
Find the vertex of the parabola: The vertex form of a quadratic function is f(x) = a(x-h)² + k, where (h, k) is the vertex. To find the vertex, use the formula h = -b/(2a) for the function f(x) = ax² + bx + c. Here, a = 1, b = -6, so h = -(-6)/(2*1) = 3. Substitute x = 3 into the function to find k: f(3) = 3² - 6*3 = -9. Thus, the vertex is (3, -9).
Determine the axis of symmetry: The axis of symmetry for a parabola is the vertical line that passes through the vertex. For this function, the axis of symmetry is x = 3.
Find the y-intercept: The y-intercept is the point where the graph intersects the y-axis, which occurs when x = 0. Substitute x = 0 into the function: f(0) = 0² - 6*0 = 0. So, the y-intercept is (0, 0).
Identify the direction of the parabola: Since the coefficient of x² (a = 1) is positive, the parabola opens upwards. This means the vertex is the minimum point of the graph.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
10mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, typically expressed in the form f(x) = ax² + bx + c. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, which can open upwards or downwards depending on the sign of the coefficient 'a'. Understanding the general shape and properties of parabolas is essential for graphing quadratic functions.
Recommended video:
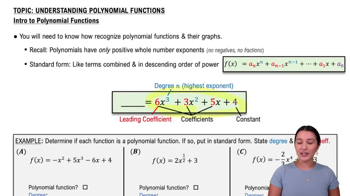
Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Vertex of a Parabola
The vertex of a parabola is the highest or lowest point on the graph, depending on its orientation. For the quadratic function f(x) = x² - 6x, the vertex can be found using the formula x = -b/(2a), which gives the x-coordinate. The corresponding y-coordinate can be calculated by substituting this x-value back into the function, providing a key point for graphing.
Recommended video:
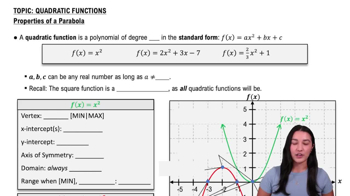
Properties of Parabolas
Intercepts
Intercepts are points where the graph of a function crosses the axes. The x-intercepts occur where f(x) = 0, and can be found by solving the equation x² - 6x = 0. The y-intercept is found by evaluating f(0). Identifying these intercepts is crucial for accurately sketching the graph of the function.
Recommended video:
Guided course
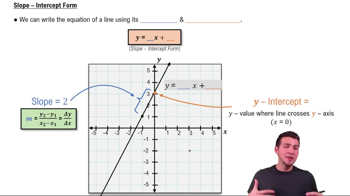
Slope-Intercept Form

 11:41m
11:41mWatch next
Master Summary of Curve Sketching with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
137
views
